What is Multi-Region SaaS Architecture and Why Does It Matter?
Multi-Region SaaS Architecture refers to a Software-as-a-Service application hosted on cloud infrastructure and deployed across multiple global regions. Instead of operating from a single location, the application runs in several data centers worldwide. This setup improves availability, reduces latency, and supports scale.
By using a multi-region approach, businesses can serve users closer to their location while keeping the service reliable. It helps maintain data consistency, meet regional compliance needs, and reduce the impact of outages. When traffic grows or a region faces an issue, the system continues to operate smoothly. Popular platforms like Netflix and Slack use multi-region deployments to deliver fast performance and high uptime to users around the world. Global education platforms also rely on this approach to provide consistent access while following region-specific regulations.
In practice, Multi-Region SaaS Architecture involves running application instances across multiple regions within cloud and multi-cloud deployment models to support:
- Load balancing for even traffic distribution
- Failover to keep services running during regional issues
- Redundancy to minimize downtime
This design improves resilience and performance while addressing challenges such as network latency, data replication, and compliance. Common techniques like distributed databases, caching, and automated failover help ensure reliable and consistent service across all regions.
How Can Platforms Ensure Scalability and High Availability in Multi-Region SaaS Architecture?
Need for Scalability
- Scalability enables applications to properly handle increasing workloads and user expectations. Explore our cloud-native microservices architecture guide to see how microservices can further improve scalability, fault isolation, and agility in cloud application development.
- Multi-region deployments serve a global user base; hence, the flexibility to expand resources across regions is required. Platforms must be built to support rapid scaling into new regions using automated provisioning, global load balancing, and multi-cloud tooling to accelerate time-to-market while controlling cost.
- Horizontal scaling, adding extra instances or nodes, is the process of sharing the workload across the application architecture.
- In a multi-region SaaS architecture, scalability also means ensuring that each region can scale independently, avoiding a single point of capacity limitation and maintaining performance consistency for global users.
Importance of High Availability:
- High availability ensures that applications are available and operational even when there are faults or disruptions.
- By distributing resources over many regions, multi-region deployments reduce the danger of a single point of failure.
- Load balancing evenly distributes incoming traffic among instances, reducing overloading and ensuring availability.
- Organizations often use DEMOactive-active vs active-passive deployment strategies with failover mechanisms to achieve near-zero downtime and meet strict SLAs. Teams also support these setups with SaaS quality management tools such as SLA monitoring, synthetic checks, and automated incident playbooks to proactively maintain uptime and reliability across regions.
Load Distribution:
- To enhance resource consumption and performance, load balancing spreads user requests across multiple instances or regions.
- It reduces reaction time, avoids bottlenecks, and improves the user experience.
- For efficient load balancing, techniques such as round-robin, least connections, and latency-based routing can be used.
- Modern SaaS platforms often use global traffic managers or DNS-based load balancing to intelligently route users to the nearest or healthiest region, further improving user experience and reducing latency.
Auto-Scaling:
- Auto-scaling adapts resources dynamically based on workload demands, helping teams maintain efficiency and control spending — explore our cloud cost optimization guide for more strategies to keep costs under control while scaling globally.
- It ensures that the application automatically scales up or down in response to traffic changes, maximizing resource utilization and cost-effectiveness.
- When and how resources are scaled are determined by scaling policies and measurements such as CPU utilization or request count.
- Predictive auto-scaling powered by AI/ML can anticipate traffic spikes (e.g., during product launches or seasonal events), enabling proactive resource allocation and preventing downtime.
Tolerance for Errors:
- Fault tolerance ensures that systems can continue to function even when components fail.
- To reduce downtime and ensure continuous operation, redundancy, replication, and failover technologies are used.
- Multi-region deployments enable geographical redundancy, where a failure in one location can be managed by redirecting traffic to another.
- Techniques such as circuit breakers, retry policies, and eventual consistency mechanisms help prevent cascading failures and maintain seamless user experience across regions.
Disaster Relief:
- Disaster recovery is concerned with the preparation and implementation of solutions for recovering from catastrophic catastrophes.
- Backups are vital, as is data replication across regions and disaster recovery sites.
- Data replication guarantees data consistency across locations, allowing for rapid recovery in the event of data loss or infrastructure failure.
- Including automated disaster recovery drills and RTO/RPO (Recovery Time Objective / Recovery Point Objective) benchmarks ensures that recovery strategies are tested and reliable when real incidents occur.
What Multi-Region Deployment Strategy Should You Choose: Active-Active vs Active-Passive?
When designing a multi-region SaaS product, one of the most critical decisions is choosing the right deployment strategy: active-active or active-passive. This choice directly affects application availability, latency, fault tolerance, and cost.
Active-Active Deployment
- Definition: All regions actively handle traffic simultaneously, sharing the load.
- Benefits:
- Maximum uptime with no single point of failure
- Optimized latency for users across regions
- Seamless failover if one region fails
-
Challenges:
- Higher infrastructure and operational costs
- Requires careful data consistency management across regions
- Use Case Example: Streaming platforms like Netflix use active-active setups to ensure uninterrupted service globally.
Active-Passive Deployment
- Definition: One region serves all traffic (active), while others remain on standby (passive) until needed.
- Benefits:
- Lower operational cost
- Simpler data replication and consistency management
- Challenges:
- Slight downtime during failover
- Latency may increase for users far from the active region
- Use Case Example: Smaller SaaS products that prioritize cost-efficiency over ultra-high availability often adopt active-passive deployment.
Key Consideration: Choosing between active-active vs active-passive deployment should balance business requirements, budget, and user experience. For enterprise-grade SaaS targeting global users, active-active deployment is usually preferred for high availability and reliability.
How Can SaaS Providers Overcome Data Replication and Consistency Challenges in Multi-Region SaaS?
Ensuring data replication and consistency in multi-region SaaS settings is critical, but it comes with hurdles. Consider the following crucial points:
- Data replication efficiency can be impacted by network latency and restricted capacity across regions.
- Concurrent modifications to the same data in multiple locations can result in inconsistencies and disputes. For multi-tenant SaaS products, implementing proper tenant data isolation & partitioning strategies helps maintain data security, avoid cross-tenant data leakage, and simplify replication consistency across regions.
- It is difficult to strike a balance between strong data consistency and low-latency access required for global users.
- These issues are common in multi-region cloud deployments, active-active architectures, and globally distributed SaaS platforms where data needs to stay synchronized across continents.
Consider the following ways for achieving data consistency across regions:
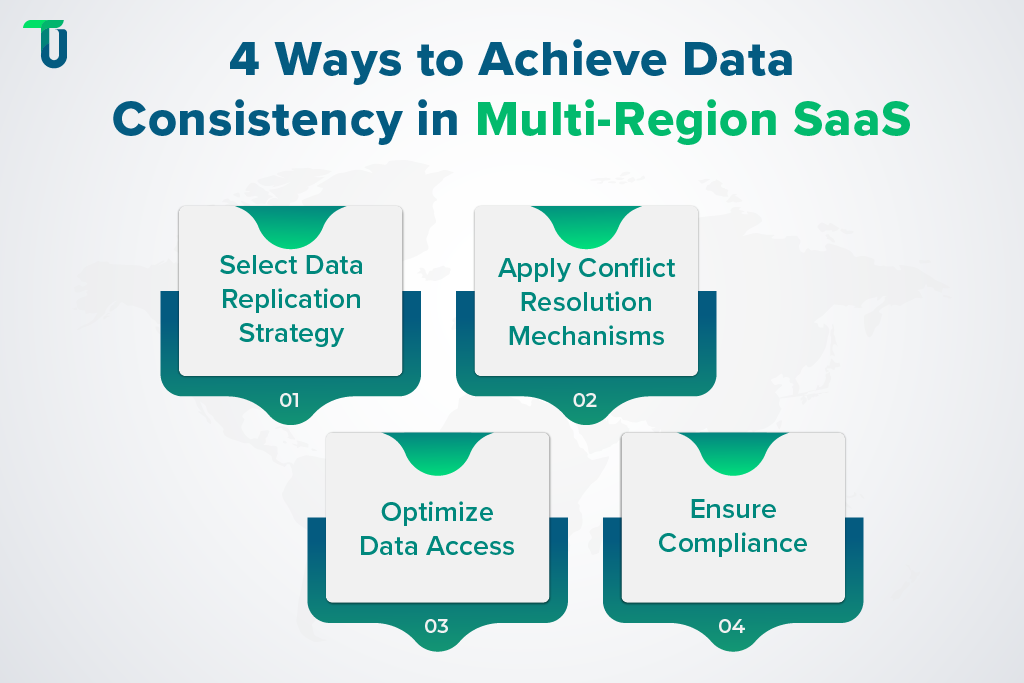
1. Choose the Right Replication Strategy
- Synchronous replication ensures that data updates are immediately synced across regions, maintaining strong consistency — but at the cost of higher write latency. Major cloud vendors also provide managed services and global databases that show how cloud providers maintain data consistency across regions, giving teams options between strong, causal, and eventual consistency models.
- Asynchronous replication allows faster writes and lower latency but may lead to temporary inconsistencies.
- Hybrid approaches such as semi-synchronous replication or quorum-based replication can balance performance with consistency for mission-critical workloads.
2. Implement Conflict Resolution Mechanisms
- To control conflicts during concurrent updates, use mechanisms such as timestamps, versioning, or last-write-wins policies.
- Advanced distributed databases (e.g., Google Spanner, CockroachDB, or DynamoDB global tables) offer multi-region consistency models and conflict-free replicated data types (CRDTs) to automatically reconcile conflicts — techniques often implemented alongside CQRS & Saga for microservices to ensure consistency and reliability in distributed systems.
3. Optimize Data Access for Performance
- Scalability, fault tolerance, and built-in replication and consistency procedures are all features of distributed databases.
- Caching methods such as CDNs and in-memory caching reduce latency by bringing frequently accessed material closer to end users.
- Use read replicas to reduce query load, apply write sharding to limit contention, and use event-driven patterns where strict consistency is not required. These approaches help keep data synchronized across regions.
- Ensure reliable data replication and access by using the right tools and processes. Centralized CMDBs, automated discovery, and sync pipelines help align asset data, remove silos, and speed up incident response and provisioning.
4. Compliance & Data Residency Considerations
When replicating data across multiple regions, organizations must comply with regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA, ensuring compliant multi-region data management and respecting data residency requirements. Use geo-fencing controls and encryption-at-rest/in-transit to secure sensitive data.
What Are the Best Practices for Optimizing Network Performance and Latency in Multi-Region SaaS Architecture?
The Influence of Network Latency on User Experience in Multi-Regional Deployments
High network latency can degrade user experience by increasing load times and response delays. In global SaaS platforms, latency above 200 ms can raise user churn and lower conversion rates, especially for real-time use cases such as video conferencing, e-learning, and SaaS quality management solutions that depend on consistent uptime and responsiveness.
Techniques for Reducing Network Latency: CDNs, Edge Caching, and Latency-Aware Routing
Techniques such as CDNs, edge caching, and latency-aware routing can be used to reduce network latency. At the application layer, SaaS queuing solutions handle global audiences by partitioning and replicating message topics, using geo-aware brokers, and routing work to regional consumers to preserve throughput and lower end-to-end latency.
- CDNs distribute content across servers in many areas, minimizing the amount of distance data must travel.
- Edge caching keeps frequently used content closer to the user, reducing round-trip time.
- Latency-aware routing chooses effective network paths dynamically depending on latency measurements, resulting in speedier data transfer.
- For multi-region SaaS applications, integrating with cloud provider Global Accelerator services (AWS Global Accelerator, Azure Front Door, GCP Cloud CDN) can route users to the nearest healthy endpoint. Using anycast routing and smart DNS-based traffic management helps ensure optimal performance for users regardless of geography.
The Importance of Reducing Round-Trip Time and Optimizing Data Transfer Between Regions
Reduce the time it takes data packets to travel between the client and server by minimizing round-trip time (RTT).
Latency is reduced by optimizing data flow across regions using compression, data deduplication, and effective routing techniques.
Request pipelining and parallel processing to improve data transfer efficiency even more.
Enterprises often adopt multi-cloud architecture SaaS or active-active deployments to serve users from multiple regions simultaneously, reducing dependency on a single data center. Leveraging private backbone networks (e.g., AWS Direct Connect, Azure ExpressRoute, GCP Interconnect) can further minimize latency for mission-critical workloads.
Continuous Monitoring & Benchmarking
Network performance requires ongoing monitoring of latency, jitter, packet loss, and throughput. Tools such as New Relic, Datadog, and Grafana help track user experience across regions and benchmark global SaaS performance.
Latency can be reduced using CDNs, edge caching, and latency-aware routing. Combined with predictive scaling, global traffic distribution, and performance benchmarking, these techniques support a resilient, low-latency SaaS platform that scales smoothly across regions.
Compliance and Security Considerations in Multi-Region SaaS Architecture
- It is critical to realize that compliance requirements and regulations differ among regions when deploying a multi-region SaaS architecture.
- When handling sensitive data, each location may have its own set of norms and standards that enterprises must follow.
- Regulations such as GDPR (Europe), CCPA (California), HIPAA (healthcare data), and SOC 2 compliance may apply depending on the industry.
- Data protection rules, privacy laws, industry-specific mandates, and other restrictions may be part of the compliance requirements.
- Enterprises must build a compliance strategy that includes region-specific data residency policies, secure APIs, and audit trails to maintain legal and ethical operations.
Security Measures for Multi-Region Deployments
- To protect sensitive data in multi-region deployments, security measures are critical.
- End-to-end encryption is necessary for safe data transmission and storage because it ensures that data is encrypted both in transit and at rest.
- Role-based access controls (RBAC) and zero-trust security models must be put in place to enforce correct authentication and authorization, limiting access to only authorized personnel.
- Regular penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and security patch automation strengthen protection against cyber threats.
- Data privacy must be prioritized, with safeguards in place to protect personally identifiable information (PII) and sensitive data.
- Please read how we applied military-grade security to a software product.
Importance of Secure Data Transmission and Storage
- Secure data transmission and storage are crucial in multi-region deployments to ensure data confidentiality, integrity, and availability (CIA triad).
- To maintain conformity to security standards and regulations, organizations should pursue compliance certifications such as ISO 27001, SOC 2 Type II, and PCI-DSS and undertake frequent audits.
- This increases client trust and displays a commitment to data security.
- Implementing secure key management systems (KMS), TLS 1.3 for encrypted communication, and multi-region backup strategies lays the groundwork for ensuring data security and limiting any risks or breaches.
Compliance & Data Residency Best Practices for Multi-Region SaaS
Deploying SaaS applications across multiple regions introduces complex compliance and data residency challenges. Every region may have its own regulations regarding data privacy, storage, and access, such as GDPR in Europe, HIPAA in the US healthcare sector, or CCPA in California.
Best Practices for Compliance in Multi-Region SaaS Deployments

Region-Specific Data Storage:
- Store sensitive data within the region it originates to comply with local regulations.
- Example: EU customer data should reside in EU data centers.
Data Replication & Consistency:
- Use synchronous replication for critical data to ensure consistency across regions.
- Use asynchronous replication for non-critical data to reduce latency.
- Implement conflict resolution strategies like timestamps or versioning.
Encryption & Access Controls:
- Encrypt data at rest and in transit.
- Apply strict role-based access controls (RBAC) to limit who can access sensitive data.
Audit & Monitoring:
- Regularly audit systems to verify compliance with global standards.
- Monitor replication logs, latency, and data integrity across regions.
Tooling:
- AWS Control Tower, Azure Policy, and GCP Data Residency tools can help enforce compliance automatically.
Checklist for SaaS Compliance Across Regions:
- Are customer data storage and backups region-specific?
- Are encryption and access policies enforced in all regions?
- Are replication strategies optimized for both performance and compliance?
- Are monitoring and audit processes automated?
Implementing these practices ensures your SaaS product not only scales efficiently across regions but also meets global compliance standards, building trust with enterprise customers.
Conclusion: Key Takeaways for Building a Robust Multi-Region SaaS Architecture
Scalability is critical: When developing a Multi-Region SaaS Architecture, applications must efficiently handle a growing and diverse global user base.
Robust cloud security: Organizations should ensure their cloud security frameworks can manage increased user demands and data loads across multiple regions while maintaining performance and compliance.
Optimized performance: Multi-region deployments must focus on network performance, fault tolerance, and data consistency to deliver seamless user experiences worldwide.
At TenUp, we specialize in designing scalable, secure, and high-performance Multi-Region SaaS Architectures. Our cloud app development expertise ensures your infrastructure can support business growth without compromising on security, compliance, or reliability.
Get in touch today to discover how our cloud app development services can help you build a resilient, globally optimized SaaS product that meets your performance, security, and compliance requirements.
Frequently asked questions
What is multi-region SaaS architecture, and why is it critical for global applications?
Multi-region SaaS architecture deploys a SaaS application across multiple cloud regions to ensure high availability, low latency, and fault tolerance. It helps global applications deliver consistent performance, comply with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA, efficiently manage traffic, and recover quickly from regional outages.
How does active-active deployment improve multi-region SaaS performance?
Active-active deployment routes traffic to all regions simultaneously, reducing latency by serving users from the nearest location and eliminating single points of failure. It ensures continuous uptime, seamless failover, and consistent performance for global users, while efficiently distributing load across regions.
What are the best practices for ensuring data consistency across multiple regions?
Ensure consistency by choosing the right replication strategy (synchronous, asynchronous, or hybrid), using distributed databases with built-in consistency, applying conflict resolution like timestamps or versioning, and leveraging caching or read replicas for faster global access. Regular monitoring and recovery plans maintain integrity across regions.
How can SaaS platforms reduce network latency for global users?
SaaS platforms reduce latency by using CDNs, edge caching, and latency-aware routing, optimizing database queries, implementing request pipelining and data deduplication, and leveraging cloud services like AWS Global Accelerator or Azure Front Door. Multi-region or multi-cloud deployments with private backbone networks further minimize round-trip time, ensuring fast and consistent global performance.
What scalability strategies should enterprises consider in multi-region SaaS deployments?
Enterprises should adopt horizontal and auto-scaling, predictive AI/ML-driven resource allocation, and region-specific capacity planning. Leveraging microservices, global load balancing, and caching ensures consistent performance, supports peak workloads, and enables seamless expansion into new regions while maintaining high availability.
How can SaaS providers comply with regional data residency and privacy regulations?
SaaS providers ensure compliance by storing sensitive data within required regions, encrypting it in transit and at rest, enforcing role-based access controls, and conducting regular audits. Leveraging cloud tools like AWS Control Tower, Azure Policy, or GCP Data Residency features helps automate compliance and maintain adherence to laws like GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA.
What tools and technologies help optimize multi-region SaaS performance monitoring?
Use observability and monitoring tools like Datadog, New Relic, Grafana, or cloud-native services (AWS CloudWatch, Azure Monitor, GCP Cloud Trace) to track latency, throughput, and availability across regions. Combine distributed tracing, synthetic monitoring, and AI/ML-powered analytics to detect anomalies, benchmark performance, and optimize global SaaS infrastructure proactively.
How can enterprises balance cost, performance, and compliance in multi-region SaaS architecture?
Enterprises can balance cost, performance, and compliance by combining deployment strategies (active-active or active-passive), auto-scaling, and multi-region data placement. Optimizing resource usage, leveraging CDNs, enforcing regional compliance policies, and adopting multi-cloud approaches ensures high performance, cost efficiency, and adherence to data residency regulations globally.

