What about fine-tuning LLMs to incorporate new information? The process is quite expensive and slow, making it impractical for keeping the models up to date with the latest information. The reliance for fine-tuning can be a big hurdle for businesses leveraging LLMs to adapt to rapidly changing situations.
In such a scenario, Retrieval-Augmented Generation(RAG) promises to be a potential solution to address these challenges by augmenting LLMs with external sources of knowledge. RAG is an innovative framework that helps LLMs by grounding the model on external knowledge sources to supplement the LLMs’ internal representation of information. This is by far a more flexible and cost-effective solution to keep AI models up to date.
What is Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and Why It Matters
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is an AI framework that boosts the performance of Large Language Models (LLMs) by retrieving real-time information from external sources. This approach ensures more accurate, up-to-date responses by combining LLMs with external knowledge, making it ideal for applications like chatbots, search engines, and decision support systems.
How Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) Works: A Step-by-Step Guide
Retrieval-Augmented Generation as the name implies has two components: a retriever and a generator.
Retriever: Finds relevant documents or passages from a knowledge base, depending on the user’s query or prompt.
Generator: An LLM that is conditioned on the retrieved data, generates the final output.
As soon as a user provides a prompt or query to the LLM, the retriever searches through the knowledge base using techniques such as dense vector similarity. It then identifies the most relevant answers, documents, or text passages that correlate to the input.
Next, the LLM is supplied with both the original prompt and the retrieved information. The LLM processes this information, grounding the response in the knowledge base content instead of using its own training data.
To further understand how RAG systems can be optimized using different database approaches, including graph and vector databases, check out our blog on Boosting AI with Graph and Vector Databases in RAG System.
Key Benefits of RAG: How It Enhances LLMs and AI Performance
Leveraging RAG for enterprise-based LLM systems offers significant advantages. RAG is particularly useful in domain-specific applications that require knowledge that’s constantly updating.
-
Cost efficiency and scale
In addition, RAG enables enterprises to scale faster. As LLMs become larger and costlier to train, RAG reduces the cost burdens. You don’t need to retrain the LLM for task-specific applications. Instead of fine-tuning on large datasets, businesses can curate well-structured external knowledge resources and update as required.
This translates into lower computational costs, improved responsiveness and enhanced data management. -
Reducing hallucinations
LLM hallucinations are events when large language models generate outputs that are coherent and grammatically correct but misleading or nonsensical, undermining the reliability of the model’s outputs. Some examples include incorrect facts, contradictions, invented information or biased statements. RAG empowers engineers to use the latest research, statistics or news. By connecting the LLM directly to the source, be it news sites, live feeds or other information sources, you get current and accurate information.
-
Developer control
Developers gain more control over the LLM’s information sources to adapt to changing requirements or cross-functional usage. They can also test and improve their applications better. It also allows them to safeguard sensitive information retrieval at various authorization levels, troubleshoot and fix if the LLM references inaccurate information sources. As a result, enterprises can use AI technology more confidently over a wider range of use cases.
Real-World Applications of RAG: Use Cases Across Industries
Well-known digital native companies and brands such as IBM, NASA, AWS, Google and several others have embraced RAG to improve their LLMs across domains. They use RAG for tasks ranging from customer support to employee training and developer productivity. Here are some of the popular use cases for RAG.
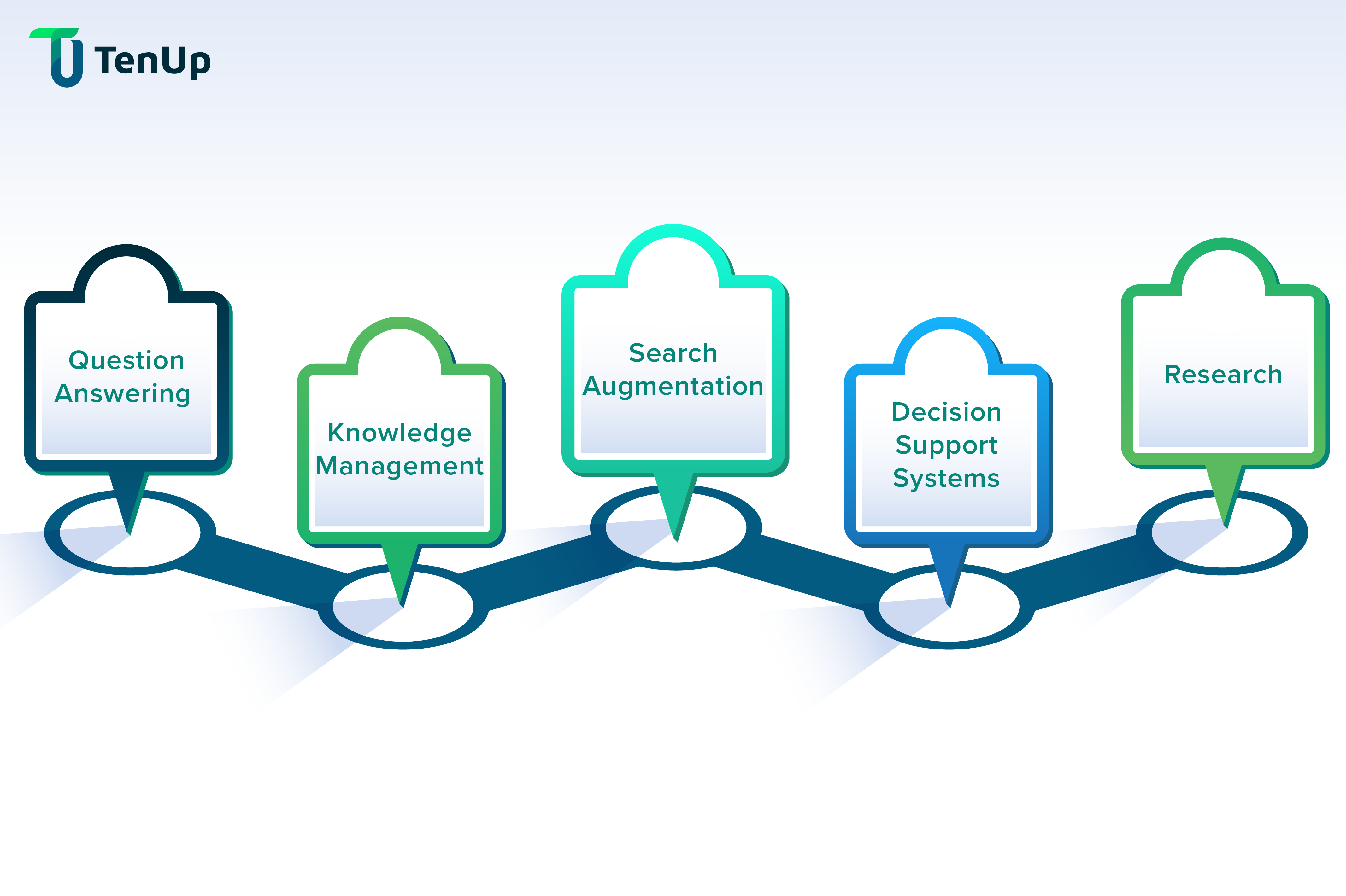
-
Question answering
Integrating LLMs with chatbots helps them to answer more accurately by retrieving answers from the company’s knowledge base. Chatbots automate customer support and website lead follow-up to resolve issues, answer queries and provide faster response.
-
Knowledge Management
RAG can drive internal knowledge databases for organizations where employees can ask complex questions to a RAG-led search system and get answers that are grounded in official documents and training material, to improve decision making and efficiency.
-
Search augmentation
Incorporating LLMs with search engines augments search results by leveraging LLM-generated answers. This integration makes it easier for users to find the information they are looking for.
-
Decision Support Systems
RAG can support decision-making processes by providing accurate and relevant information, analyzing different perspectives or scenarios, and generating insights or recommendations to aid in decision-making.
-
Research
RAG can accelerate research and development across various fields by providing insights into a vast amount of relevant literature, in generating hypotheses or research questions, aiding the analysis and interpretation of R&D initiatives.
RAG is already being leveraged by companies to turn technical or policy manuals, videos or logs into knowledge bases that improve their LLM. Companies have noted significant improvements in the accuracy and reliability of their LLM-based systems after integrating RAG. IBM launched its new AI and data platform watsonx, which offers RAG.
Real-world examples demonstrate the effectiveness of RAG in improving the performance of LLMs. Companies have reported significant improvements in the accuracy and reliability of their LLM-based systems after implementing RAG. Case studies highlight how RAG has been successfully applied in various domains to address specific challenges and enhance the capabilities of LLMs.
Conclusion
LLMs are here to stay and their capabilities and applications will get only more powerful with time. However, relying solely on internal knowledge or parametric knowledge can lead to factual errors and outdated information. RAG is a significant advancement in natural language processing, addressing the shortcomings of LLMs. The RAG framework supplements LLMs with external sources of information, allowing models to provide more accurate and current responses. As RAG evolves, LLMs can unlock their full potential driving innovation across industries and use cases. We provide NLP services as a part of our comprehensive Artificial Intelligence services . Our experienced AI engineers can help with your LLM issues.
Contact us today.

