What Is a Cloud Deployment Model?
A cloud deployment model explains where your data, apps, and services run and who has control over them. It helps decide how secure, flexible, and cost-effective your setup can be. There are four main cloud deployment models you should know about:
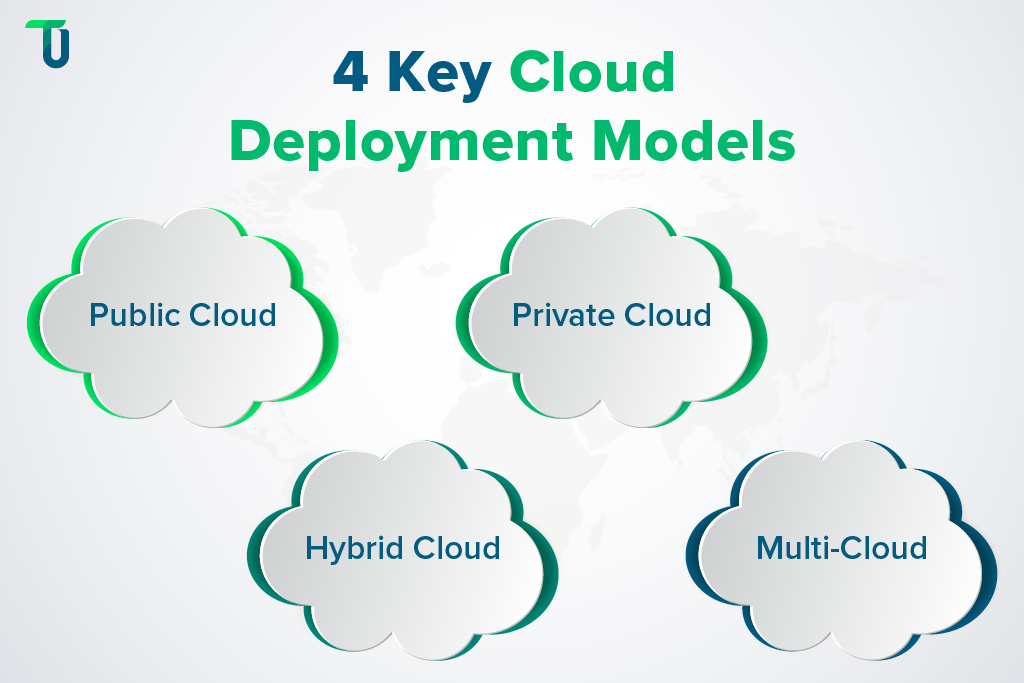
- Public cloud: A provider owns and manages the resources, and anyone can use them.
- Private cloud: Only one company uses the infrastructure, so it offers better control and security.
- Hybrid cloud: It mixes public and private clouds, allowing movement of data between the two.
- Multi-cloud: It uses multiple cloud providers to avoid depending on just one.
Each model fits different business needs. For example, the public cloud is affordable and scalable, whereas the private cloud offers better privacy. On the other hand, the hybrid cloud model brings flexibility, while the multi-cloud model adds reliability with more options.
Did You Know? Amazon Web Services (AWS) introduced the first widely adopted public cloud platform in 2006, changing how businesses manage IT infrastructure.
Public Cloud Model: Overview, Benefits, and Drawbacks, Best Use Cases
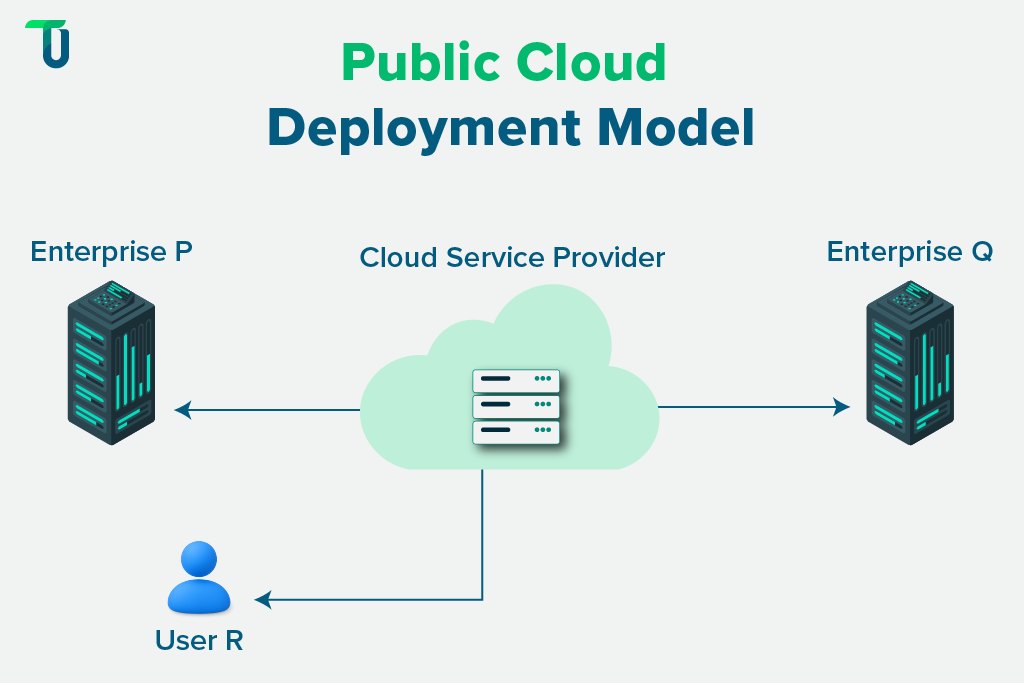
The public cloud model is a type of cloud deployment model where services are offered by third-party providers over the internet. It allows businesses to access computing resources without managing physical infrastructure. This model is flexible, cost-effective, and suited for many use cases.
Advantages of Public Cloud Model
- Pay-as-you-go pricing helps reduce upfront hardware expenses
- Fast scaling to meet sudden spikes in user demand
- No need to manage software updates or system maintenance
Disadvantages of Public Cloud Model
- Shared infrastructure may raise data security concerns
- Usage can grow costs quickly without proper monitoring
Best Use Cases for Public Cloud Model
Public cloud works best for dynamic and general workloads where flexibility matters. Here are a few notable use cases:
- Hosting websites or web apps with unpredictable traffic
- Running development or testing environments
- Storing backups or archived data offsite
- Supporting e-commerce platforms with seasonal load changes
- Powering mobile or SaaS applications needing quick rollout
The public cloud offers a balance of convenience, speed, and cost savings. It's ideal for many businesses, but it's important to assess workload needs and security before choosing this model.
You Might Also Like
Private Cloud Model: Overview, Benefits, and Drawbacks, Best Use Cases
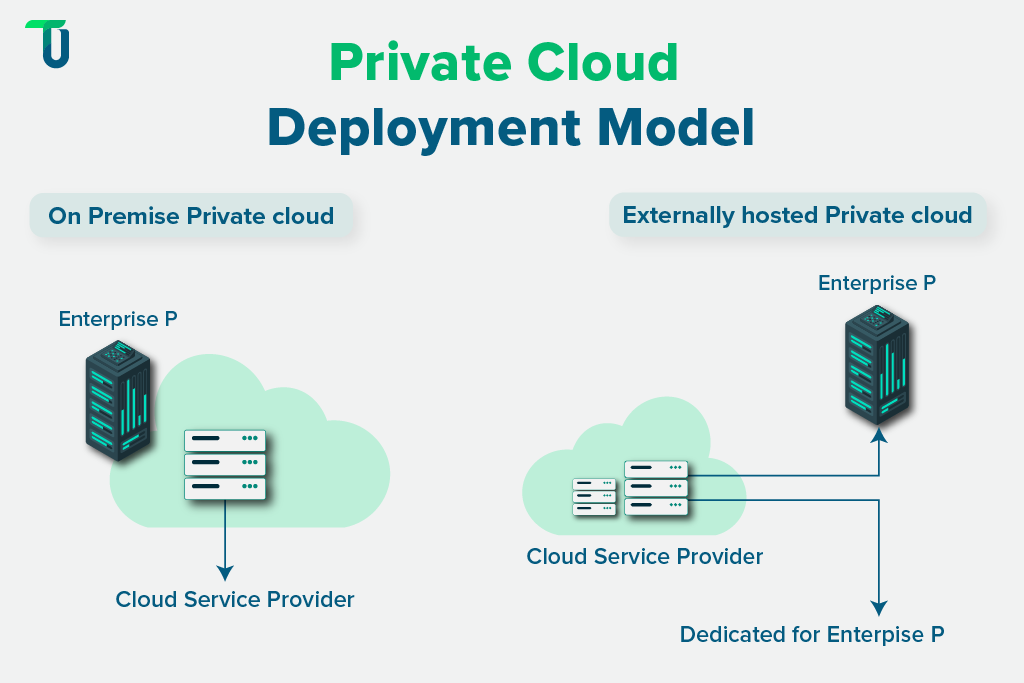
The private cloud is a type of cloud deployment model where computing resources are dedicated to a single organization. These resources can be hosted on-premise or by a third party. Unlike the public cloud model, the private cloud model offers greater control, privacy, and customization, making it suitable for companies with strict security or compliance needs.
Advantages of Private Cloud Model
- Complete control over data, applications, and security settings
- Meets compliance needs for regulated industries or sensitive data
- Custom configurations to match specific business or technical needs
Disadvantages of Private Cloud Model
- Higher upfront and maintenance costs compared to shared models
- Limited scalability unless more physical infrastructure is added
Best Use Cases for Private Cloud Model
Private cloud works best for organizations that need high security, control, or compliance. Here are a few typical use cases:
- Storing sensitive financial or healthcare data
- Supporting government or defense-related operations
- Running legacy applications not suited for public cloud
- Hosting internal business systems that need strict access control
- Managing workloads with fixed performance and resource needs
The private cloud suits businesses that value control and data protection over cost savings. It is not the most flexible model, but for security-focused workloads, it offers clear advantages.
Get Expert Help Choosing Your Cloud Model
Don’t leave cloud strategy to guesswork. Let TenUp guide you toward a secure and scalable cloud foundation.
Hybrid Cloud Model: Overview, Benefits, Drawbacks, Best Use Cases
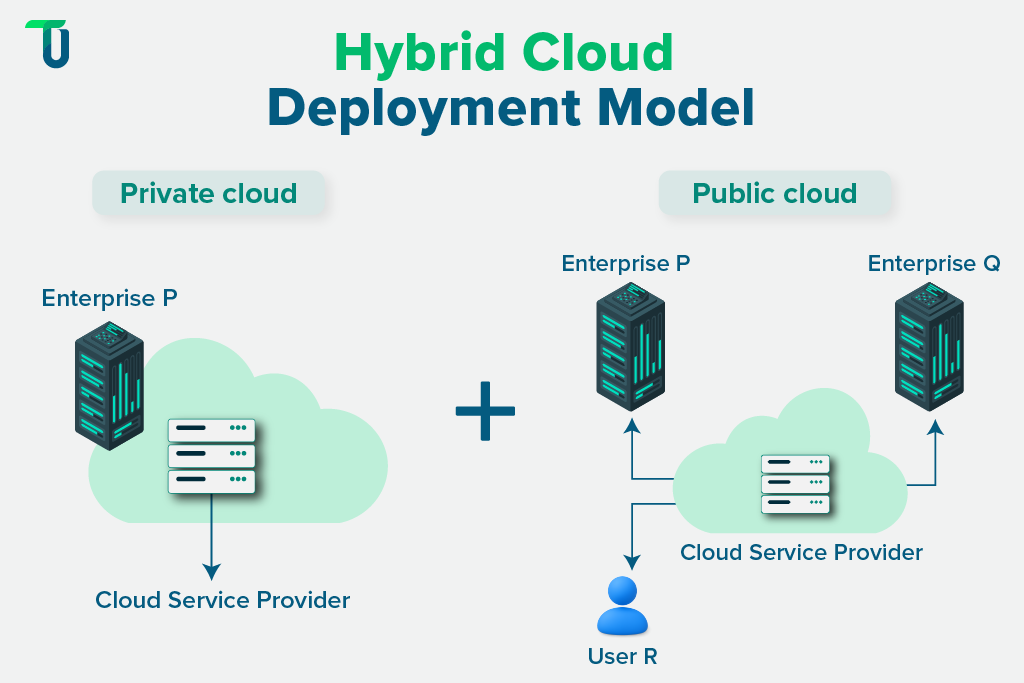
The hybrid cloud model is expected to become the default model for 90% of large organizations by 2027. It is a cloud deployment model that links private and public cloud resources. It gives businesses the freedom to place sensitive data in a secure private setting, while using scalable public services for general workloads. This mix aims to balance control and cost effectively, helping enterprises stay flexible and competitive, especially when supported by Cloud solutions for rapid innovation and resilience.
Advantages of Hybrid Cloud Model
- Balances security of private cloud with flexibility of public cloud
- Supports gradual cloud adoption without full infrastructure shift
- Allows sensitive data to stay on-premise while using public resources
Disadvantages of Hybrid Cloud Model
- Complex setup and integration between public and private systems
- Requires strong IT management to ensure proper data flow and security
Best Use Cases for Hybrid Cloud Model
Hybrid cloud works best for businesses that need both control and scalability. It helps manage varying workloads while keeping sensitive operations protected.
- Running critical apps in private cloud while using public cloud for testing
- Storing confidential data privately while using public cloud for analytics
- Handling sudden traffic spikes using public cloud overflow
- Supporting disaster recovery plans with a backup in public cloud
- Enabling remote teams to access resources without full public exposure
As we can see, the hybrid cloud model offers a mix of control and convenience. It fits companies with strict data rules or changing workload needs. By using the strengths of both private and public setups, businesses can stay flexible while keeping core systems secure.
Multi-Cloud Model: Overview, Benefits, Drawbacks, Best Use Cases
The multi-cloud is a type of cloud deployment model where a business uses services from more than one cloud provider. It combines public or private cloud platforms from different vendors. This model helps avoid reliance on a single provider and offers more control over specific workloads.
Advantages of Multi-Cloud Model
- Reduces vendor lock-in and adds more deployment flexibilit
- Improves reliability by avoiding full dependency on one provider
- Allows best-fit services from each provider based on workload needs
Disadvantages of Multi-Cloud Model
- Managing multiple providers increases complexity and cost
- Data movement across platforms may lead to performance issues
Best Use Cases for Multi-Cloud Model
The multi-cloud model is ideal for large organizations with complex or diverse IT needs. Here are some use cases:
- Running critical apps on different clouds for higher availability
- Meeting regional compliance by choosing providers based on location
- Balancing workloads to avoid service disruptions or downtime
- Using one provider for AI tools and another for storage or databases
- Reducing risks by spreading cloud resources across multiple vendors
The multi-cloud approach gives businesses more freedom and control. It helps meet technical, legal, or performance requirements across different regions or teams — and you can learn how Supercloud integrates various deployment models to make this even more efficient.
Public Vs Private Vs Hybrid Vs Multi-cloud Model: A Quick Comparison
Take a look at the table below to quickly understand how public, private, hybrid, and multi-cloud models compare.
| Feature | Public Cloud | Private Cloud | Hybrid Cloud | Multi-Cloud |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ownership | Third-party provider | Single organization | Combination of both | Multiple cloud providers |
| Access | Shared with many users (public) | Used by one organization only | Mix of public and private access | Uses several public/private clouds |
| Cost | Low upfront cost, pay-per-use | Higher cost due to dedicated setup | Balanced cost | Varies based on setup and providers |
| Security | Basic, depends on provider | High, full control | Better than public, less than private | Depends on provider and configuration |
| Scalability | Very high | Limited to private resources | Scales well across both | High, but can be complex to manage |
| Control | Low | Full control | Partial control | Varies by provider and workload |
| Best For | Startups, general apps, testing | Banks, healthcare, regulated sectors | Enterprises needing flexibility | Large firms with diverse IT needs |
As we can see, each cloud model has its own strengths, but long-term success depends heavily on cloud-based data storage reliability and availability across all deployment strategies. Public cloud offers flexibility at lower cost, private cloud gives full control, hybrid cloud balances both, and multi-cloud avoids reliance on a single provider. Choose the one that best fits your security needs, budget, and workload goals.
Choosing the Right Deployment Model: Key Factors
Choosing the right deployment model depends on your organization’s goals, budget, and security needs. For example, choose:
- Public Cloud: When you need quick setup, lower costs, and scalability without managing infrastructure.
- Private Cloud: When handling sensitive data, requiring strict control, or meeting specific compliance standards.
- Hybrid Cloud: When you need both public cloud flexibility and private cloud control, especially for varying workloads.
- Community Cloud: When multiple organizations with shared concerns (like compliance or mission) collaborate on a joint infrastructure.
Remember that each model serves different needs. There is no one-size-fits-all solution. Evaluate your technical requirements, internal expertise, and long-term strategy — or refer to our CTO checklist for custom cloud application development best practices for a structured approach. Also, review any legal or industry-specific rules that may affect your deployment choice.
Simplify Cloud Deployment Models Selection with TenUp
Choosing the right cloud deployment model helps your business stay secure, flexible, and cost-efficient. However, many companies face real challenges such as managing high costs, protecting sensitive data, or migrating systems smoothly to the cloud. Without the right support, these issues can slow progress or lead to costly mistakes.
That’s where TenUp Software Services comes in. We are an ISO 27001-certified company and an official AWS partner, backed by a skilled team with expertise in cloud migration, cost optimization, and secure system design.
Get in touch with our expert today to select the right cloud model and ensure a successful implementation.
Choose the Right Cloud Model with TenUp
From strategy to execution, TenUp ensures secure, cost-effective cloud deployments tailored to your needs.
Frequently asked questions
How much does it typically cost to migrate from private to public or hybrid cloud?
Cloud migration typically costs between $5,000 and $100,000, depending on data size, app complexity, and the migration method. Costs include infrastructure, app changes, and consulting. Public cloud is more affordable; Hybrid Cloud offers cost-control flexibility. Use tools like AWS Migration Hub or Azure Migrate for better planning.
What migration tools and platforms support hybrid or multi-cloud environments?
Leading tools include VMware HCX, Azure Migrate, AWS Migration Hub, and Carbonite Migrate for workload transfers. For monitoring and optimization, use Datadog or Turbonomic. These platforms help manage migrations and performance across on-premise and cloud environments.
Can performance and latency issues arise in hybrid clouds, and how to optimize them
Yes, latency can occur due to the distance between on-premise and cloud environments. To reduce it, use dedicated connections (like AWS Direct Connect), CDNs to cache content closer to users, and monitor traffic paths to prioritize critical workloads. Right-sizing resources and using edge computing can further boost performance.
What strategies are effective for avoiding vendor lock-in in multi-cloud deployments?
To avoid vendor lock-in, use open-source tools like Kubernetes and Terraform, avoid provider-specific services, and design apps using portable containers with abstraction layers for compute, storage, and networking. Standardize APIs and ensure data portability to stay flexible across clouds.
What are common security pitfalls when operating in hybrid or multi-cloud environments?
Security risks include misconfigured IAM roles or firewalls, inconsistent policies across providers, unencrypted data transfers, and lack of centralized visibility. These gaps can lead to data breaches or compliance failures. To mitigate them, use unified IAM, encrypt all traffic, and deploy SIEM tools for real-time threat detection and monitoring.
When is community cloud a better choice than private, hybrid, or public cloud?
Community cloud is ideal when multiple organizations share regulatory needs (like in healthcare or government), have a common mission, and want to cut costs by sharing infrastructure. It balances security, compliance, and collaboration—making it more efficient than managing separate private or hybrid setups.
How do blue–green or canary deployment strategies fit into different cloud models?
Both strategies work best in the public cloud using tools like AWS ELB or Azure Traffic Manager. Private clouds support them with custom setups (e.g., Jenkins, Spinnaker). In hybrid/multi-cloud, they enable zero-downtime and staged rollouts but need strong traffic orchestration and rollback planning.
Which type of cloud deployment model uses both public and private clouds, allowing you to run workloads on either and have them work seamlessly together?
Hybrid cloud deployment combines public and private clouds, giving organizations the flexibility to run workloads on either environment. Both environments are integrated, enabling seamless movement of data and applications and unified management. Hybrid cloud is ideal for balancing scalability, security, and compliance.

