Public vs. Private Cloud: Which Cloud Model Should Your Business Choose?
Public and private clouds are two core types of cloud-based deployment, each offering unique benefits depending on your business needs. Let's take a brief look at how they differ.
What is a public cloud deployment model?
What Is Public Cloud? Benefits, Use Cases & When to Choose It
A public cloud is a cloud-based deployment where a third-party provider offers computing resources over the internet. It uses shared infrastructure to serve multiple users at once.
Public cloud uses shared infrastructure to deliver flexible, pay-for-use computing—ideal for web scaling, Dev/Test environments, and businesses seeking low upfront investment, such as when building a SaaS-based wealth management platform.
Here are the main advantages:
- You only pay for what you use. There’s no need to buy or manage physical servers.
- You can increase or reduce resources quickly to match demand.
- Redundant systems across regions help reduce downtime.
In summary, public cloud works well for fast, flexible, and cost-efficient solutions.
What is a private cloud deployment model?
A private cloud uses a dedicated infrastructure built for one organization. It can be managed in-house or hosted by a provider but remains isolated from other users. Private cloud offers single-tenant, isolated infrastructure with full control, ideal for sensitive data, compliance-heavy industries, and performance-critical apps.
Key benefits include:
- You manage hardware, network, and settings based on your needs
- It supports strict security and compliance requirements.
- Dedicated resources ensure stable and consistent performance.
To conclude, private cloud fits best when control, security, and reliability are top priorities.
You Might Also Like
Key Benefits And Drawbacks of Public Cloud Deployment
Public cloud deployment offers a fast, flexible way to host applications and data via cloud‑based deployment. You gain many benefits. Yet, it's not perfect. Let’s see both sides directly.
Key Advantages of Public Cloud Model
Cost efficiency: You pay only for used resources. This removes upfront spending. You scale resources when demand rises without heavy investment in hardware.
On‑demand scaling: You can add CPU, RAM, storage instantly. This flexibility helps during demand peaks. There’s no need to buy extra physical servers.
Minimal maintenance: Provider handles updates, hardware fixes, security patches, and spare parts. Your team avoids those chores and focuses on core tasks.
Global reach: You deploy services near users worldwide. That cuts latency. Data can stay within legal regions. You avoid building data centers abroad.
Reliable uptime: Providers use redundant servers and availability zones. Failures on one machine don’t stop your service. Systems stay live most of the time.
Major Disadvantages of Public Cloud Model
Security risks: You share infrastructure. Sensitive data may sit on shared servers. You rely completely on the provider's encryption and protections.
Cost unpredictability: Pay‑as‑you‑go is flexible, but costs vary. Without careful tracking, monthly bills can spike unexpectedly due to unused or memory‑heavy instances.
Limited customization: You use standard settings. Deep network or hardware tweaks aren’t allowed. Providers limit modifications. That may hinder niche or legacy needs.
As we can see, while cloud-based deployment in a public cloud offers clear benefits like cost savings and flexibility, it also comes with trade-offs in control, security, and predictability. Choose wisely.
Confused Over Complex Cloud Decisions?
Get guidance through cloud-based deployment with expert insights and tailored architecture solutions.
Key Benefits And Drawbacks of Private Cloud Deployment
Private cloud deployment provides a secure, dedicated way to host applications and data via cloud-based deployment. You get full control and customization. Still, it has its downsides. Let’s look at both sides clearly.
Key Advantages of Private Cloud Model
Enhanced security: Only your organization accesses the setup. Data stays on private servers. You control users, encryption, and every layer of protection.
Fixed costs: You invest in infrastructure once. Costs stay stable over time. No surprise bills based on monthly usage or traffic spikes.
Full customization: You set everything up as needed. This suits legacy apps or systems that need special configurations or hardware.
Regulatory control: You know where your data lives. It’s easier to meet industry rules or audits. You control compliance, not the provider.
Reliable performance: No one else shares the environment. This avoids slowdowns or unpredictable workloads caused by others on the same server.
Major Disadvantages of Private Cloud Model
High upfront costs: You need to buy hardware, set up data centers, and manage resources. It demands bigger spending at the start.
Maintenance effort: Your team manages updates, repairs, backups, and security. That adds pressure and requires in-house expertise.
Less flexibility: You can’t scale instantly. Adding capacity means buying more hardware, which delays growth during sudden demand.
As we can see, while cloud-based deployment in a private cloud ensures control, security, and stability, it also brings higher costs, more upkeep, and slower scaling. Choose wisely.
Core Differences: Public vs. Private Cloud Deployment Models
Take a look at the table below that highlights nine key differences between public and private cloud, covering cost, control, scalability, and technical aspects of cloud-based deployment models.
| Feature | Public Cloud | Private Cloud |
|---|---|---|
| Deployment | Shared across multiple users | Dedicated to one organization |
| Cost | Pay-as-you-go pricing | High upfront, stable over time |
| Security | Standard controls, shared infrastructure | Full control, stricter security |
| Scalability | Quick and flexible scaling | Hardware-dependent scaling |
| Maintenance | Managed by provider | Handled internally |
| Network Control | Limited, predefined by provider | Full control over routing and firewalls |
| Storage Options | Standardized options | Custom storage based on workload |
| Resource Isolation | Virtual isolation via hypervisors | Physical and logical separation |
| Compliance | Meets general standards (e.g., ISO) | Supports strict industry regulations |
All in all, while public cloud offers flexibility and lower upfront costs, private cloud ensures greater control, security, and customization.
Real-World Examples of Public and Private Cloud Deployment Models
To better understand how cloud-based deployment works in real life, let's look at real-world examples of both public and private cloud models.
Examples of Public Cloud Deployment
Here are some notable examples of public cloud deployment that show how organizations use shared infrastructure.
1. Netflix on AWS
Netflix uses AWS to handle massive video streaming demands. It adjusts computing power based on user traffic, ensuring smooth playback. This cloud-based deployment removes the need for in-house servers and helps Netflix deliver reliable, global service.
2. Airbnb on AWS
Airbnb uses AWS infrastructure to support its travel platform. It scales servers up or down based on booking trends. This approach avoids hardware costs and keeps the app responsive during demand spikes, making operations more flexible and efficient.
3. Yandex Cloud
Yandex Cloud provides public cloud services such as storage, compute power, and networking. Businesses use it for cloud-based deployment to access resources remotely. It supports a range of industries looking for scalable, on-demand infrastructure.
Examples of Private Cloud Deployment
Below listed are some notable examples of private cloud deployment that highlight how companies use dedicated environments.
1. CIA private cloud by Amazon
Amazon designed and operates a private cloud for the CIA within its own secure data centers. This setup ensures full control and protects classified data by keeping all computing and storage entirely inside the government’s physical infrastructure.
2. NYSE private cloud
The New York Stock Exchange runs a private cloud built with VMware vCloud at its New Jersey facility. This allows financial firms to create virtual servers while keeping sensitive trading data local, supporting speed, security, and compliance.
3. Bank private storage clouds
Banks often use private cloud environments set up within their own buildings. These systems are restricted to internal teams and are used to safely store and process customer data while meeting strict industry regulations and avoiding external network exposure.
Real-World Examples of Cloud Service Models
Cloud service models help businesses run software, build apps, or manage infrastructure through the internet. Here are three real-world examples– one for each service model, that show how different industries use cloud-based deployment to meet their needs.
1. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Example: Amazon EC2
Amazon EC2 offers virtual servers on demand. Companies use it to run websites, apps, or large systems without owning physical hardware. It allows complete control over the OS and storage. EC2 supports cloud-based deployment, helping teams scale quickly during traffic spikes.
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Example: AWS Elastic Beanstalk
Elastic Beanstalk lets developers upload code and launch web apps. AWS manages the infrastructure, load balancing, and updates. It reduces setup time and allows faster app rollouts through cloud-based deployment.
3. Software as a Service (SaaS)
Example: Google Workspace
Google Workspace offers email, documents, meetings, and storage through a browser. It requires no setup or updates from the user. The entire system runs on a cloud-based deployment, making it easy to access from any device.
Also Read: SaaS vs. PaaS vs. IaaS: Understanding Types of Cloud Based Applications
How to Choose the Right Cloud Model for Your Business?
Choosing the right cloud model requires a clear understanding of your business needs, budget limits, security concerns, and technical resources. Here's how:
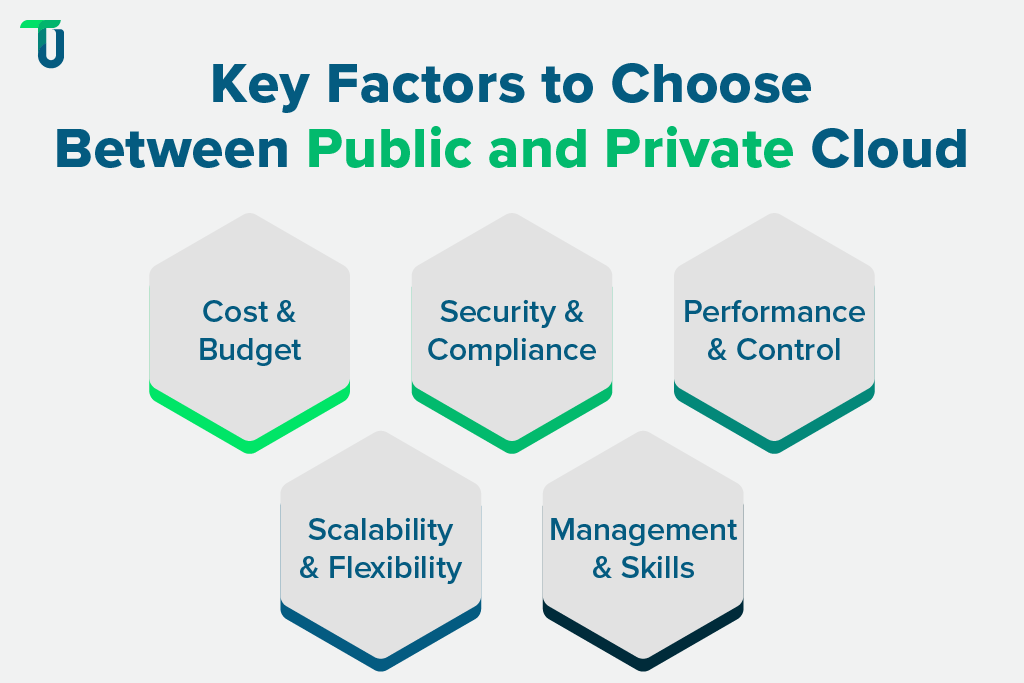
1. Cost and Budget
Start with what you can afford. Public cloud offers a low-cost entry with pay-per-use. Private cloud needs a bigger upfront investment but provides more control. Hybrid cloud helps balance cost by running sensitive data privately while using public cloud for the rest.
2. Security and Compliance
If your industry handles confidential data, this factor is critical. Private and hybrid cloud models give better control over data and support compliance rules. Public cloud can still be secure, but it depends on your provider’s shared responsibility model.
3. Performance and Control
Performance needs vary. Private cloud gives full control and steady performance. The public cloud model may face slowdowns during high usage. Hybrid cloud helps by keeping critical workloads in-house and pushing lighter ones to the public cloud.
4. Scalability and Flexibility
If you expect to grow fast, the public cloud model is ideal for quick scaling. Hybrid and multi-cloud offer flexibility to shift workloads based on changing needs. They also help prevent dependency on a single provider. For businesses looking to maximize efficiency and control across multiple clouds, Optimize Your Multi-Cloud Strategy with Supercloud provides practical real-world use cases to guide your approach.
5. Management and Skills
Choose a model that your team can handle. Public cloud model is easy to manage. Private and hybrid clouds require in-house skills and effort. Multi-cloud setups need solid coordination and policy enforcement.
To sum up, choose a cloud model that fits your budget, data needs, performance goals, and team skills.
Cloud-based Deployment: Best Practices
In order to get the maximum benefit from cloud-based deployment, organizations should follow proven practices to ensure reliable, secure, and efficient delivery. Here are six core areas to focus on:

1. Automate Provisioning With IaC Tools: First, use infrastructure as code tools such as Terraform or AWS CloudFormation. These let teams define servers and networks in code. Consequently, deployments stay consistent and repeatable.
2. Use Load Balancing and Auto Scaling Features: Next, configure cloud load balancing and autoscaling. These ensure apps handle traffic peaks without downtime. Also, autoscaling replaces unhealthy instances automatically.
3. Secure Infrastructure With Strong Controls: Then, apply strong authentication and encrypt data at rest and in transit. In addition, use network segmentation and restrict access with least privilege policies.
4. Embed Tests in CI/CD Pipeline: Also, integrate security and functionality tests early in your CI/CD process. Automated scans, code reviews, and access controls reduce risks and improve stability.
5. Monitor Performance and Cost Usage: Furthermore, implement real-time monitoring and alerting. Likewise, track cost metrics and set budgets to avoid overspending. Regular reviews reveal improvement opportunities.
6. Log Activity and Audit Regularly: Finally, enable centralized logging and audit trails. This approach helps detect anomalies, ensure compliance, and simplify troubleshooting.
By applying these six concrete practices, teams deliver resilient systems that adapt to change, remain secure, and keep costs under control.
Find the Right Cloud Deployment Model With TenUp
Both public and private cloud models have their own advantages. But the right one for your business depends on your goals, technical needs, and any rules you must follow. For most growing businesses, it’s not always easy to choose between the two. Each option has trade-offs when it comes to cost, control, and flexibility. That’s where TenUp can help.
As a trusted cloud partner, we at TenUp make things simpler. We are ISO 27001 certified and an official AWS Consulting Partner. Our team knows how to build secure and scalable cloud systems. We help you choose the right model and set it up in a way that fits your business perfectly.
Need Seamless Cloud Deployment?
From planning to execution, TenUp ensures your cloud journey is secure, scalable, and aligned with your business goals.
Frequently asked questions
What exactly defines a “private cloud” vs. “on‑premises"?
Private cloud delivers cloud-like features—self-service, scalability, and automation—whether hosted on-site or off-site. On-premises refers to traditional, in-house infrastructure, often lacking those dynamic capabilities. Key difference: private cloud behaves like cloud; on-premise is just owned hardware without elasticity.
Is a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) the same as a private cloud?
No. A VPC is a logically isolated slice of a public cloud, offering privacy at the network level—but it still runs on shared infrastructure. A private cloud, by contrast, is a dedicated, single-tenant environment, offering full control and isolation.
Which is more cost-effective: small public cloud vs. building a small private cloud?
Public cloud wins for small-scale needs—its pay-as-you-go model avoids upfront costs and offers flexibility. A private cloud may only be cheaper if workloads are steady, high-volume, and your team can manage the infrastructure efficiently.
Can private clouds offer the same scalability and elasticity as public clouds?
Not by default—but yes, if designed right. Private clouds using cloud-native platforms (e.g., OpenStack, Kubernetes) and automation can scale on demand, though public clouds still lead in speed and global resource availability.
Is the public cloud always less secure than the private cloud?
Not always. Public clouds offer advanced security, 24/7 monitoring, and compliance certifications. Private clouds provide isolation and control—but both are only as secure as their configurations, access policies, and encryption practices.
How do I choose between public and private cloud for Dev/Test vs. production workloads?
Use a public cloud for Dev/Test—it's fast, flexible, and cost-effective. Choose a private cloud for production when security, compliance, or performance consistency is critical. For mixed needs, a hybrid approach balances agility with control.
Can small teams benefit from private clouds, or is public cloud always better for them?
Public cloud is usually better for small teams due to its low cost and simplicity. But if you need strict security, stable workloads, and have the skills to manage infrastructure, a private cloud can still be a smart fit.
Which cloud deployment model suits a mid-sized e-commerce company with rapid growth, seasonal traffic spikes, limited budget, and willingness to accept shared infrastructure risks?
The public cloud deployment model is the best fit. It offers on-demand scalability, pay-as-you-go pricing with minimal upfront investment, and reliable security controls. While resources are shared with other customers, public clouds deliver elastic capacity and significant savings, making them ideal for e-commerce sites that need to manage traffic spikes on a tight budget.

