Cloud Application Development: An Overview
Cloud application development is the process of creating software applications that are deployed and run in cloud environments, such as AWS, Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud, rather than on-premises servers. These applications are accessible over the internet and benefit from the scalability, resilience, and global reach of cloud infrastructure.
This process is also referred to as cloud-native application development, where apps are designed specifically for distributed cloud systems using modern practices like microservices, containerization, and DevOps.
Moreover, companies can opt for custom cloud application development to tailor solutions to their needs. These custom apps adjust as demand grows, remain flexible, and stay secure. In addition, services like Platform as a Service (PaaS) and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) simplify deployment, accelerate time-to-market, and reduce overhead.
Overall, cloud application development delivers elastic scalability, cost control, and performance for modern digital software initiatives. It's a critical part of digital transformation strategies across industries like fintech, healthcare, eCommerce, and logistics.
Understanding Microservices Architecture
Microservices architecture splits a large cloud-native application into small, independent services that each focus on one specific business capability or domain task. Each service runs its own codebase, manages its own data storage, and can be developed, deployed, and scaled independently. They communicate with one another through lightweight, RESTful APIs or event-driven messaging systems like Kafka.
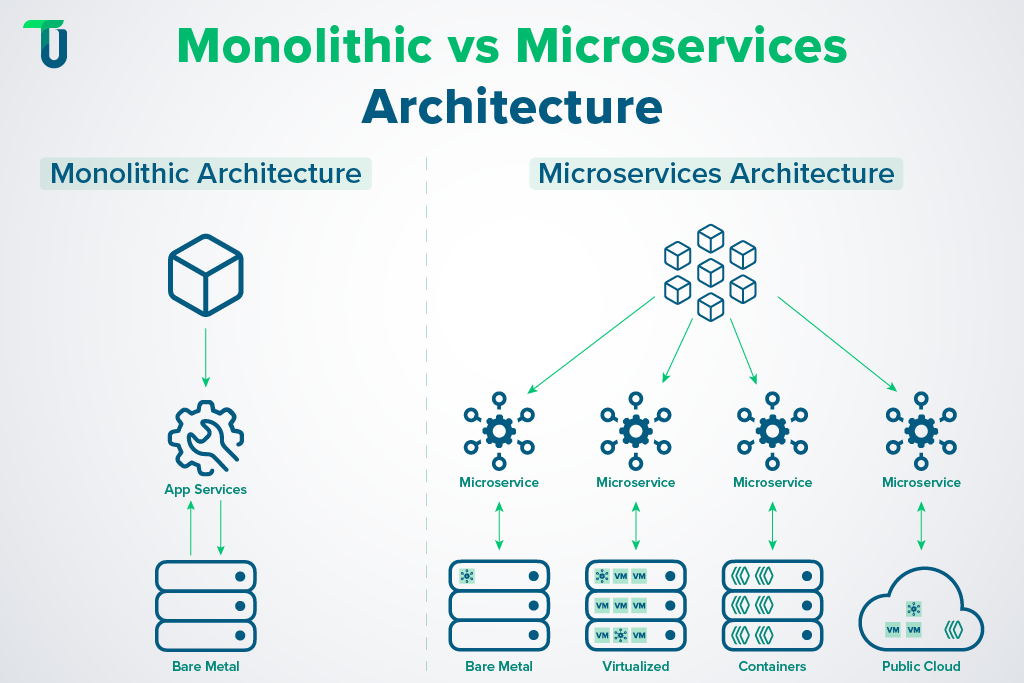
This distributed architecture significantly boosts scalability because you can scale only the high-traffic or resource-intensive components instead of the entire application. Moreover, it improves resilience and fault isolation, since a failure in one service does not bring down the whole system. Microservices also enhance team agility—small, cross-functional teams can independently build, test, and deploy services, which accelerates development velocity and supports continuous delivery (CD).
However, this setup does introduce operational complexity, particularly in areas like service discovery, API gateway management, distributed logging, data consistency across services, and cloud storage performance metrics. Using tools like Kubernetes, service meshes, and centralized observability platforms can help manage these challenges.
Build Scalable Cloud Apps from Idea to Execution
Get full-cycle support for custom cloud application development, from planning to deployment and beyond. Talk to our Cloud expert today!
Why Microservices Matter in Cloud Application Development
Microservices play a major role in how startups can build scalable cloud applications by breaking complex systems into smaller, modular parts that support agility, resilience, and growth. This modular architecture supports scalability, agility, and resilience—three core principles of building modern cloud-native applications that help organizations fully leverage the benefits of cloud-native solutions.
Here are five key reasons that make them essential for building reliable and future-ready cloud apps.
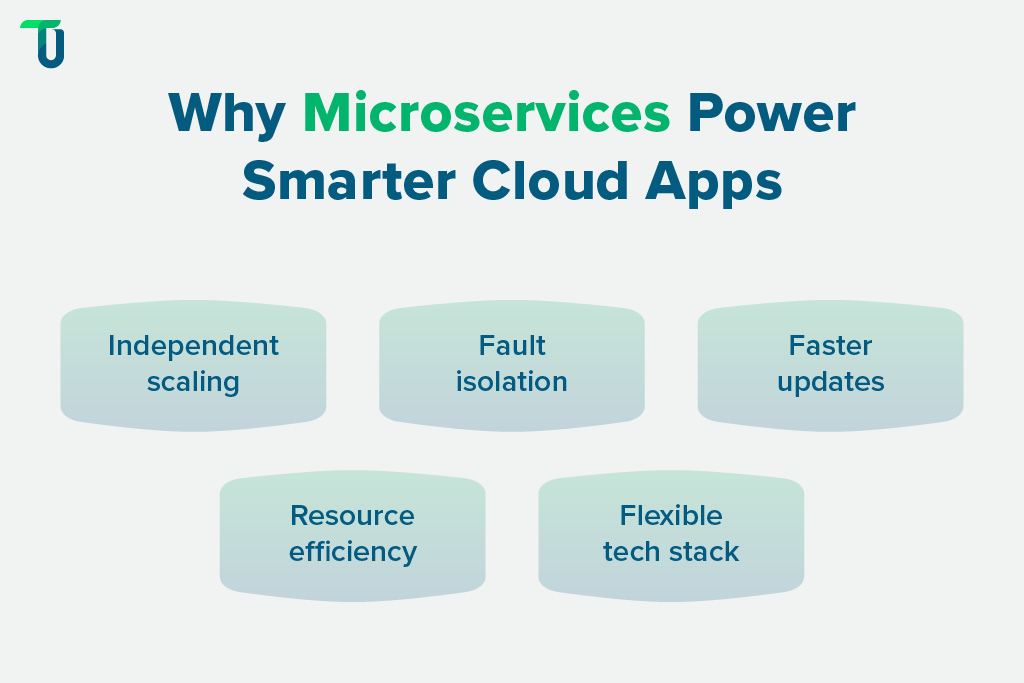
1. Better Scalability for Each Service
With microservices, you don’t have to scale the entire application at once. Each service runs on its own, so you can dynamically scale only the part that gets more traffic. This helps save cloud resources and reduce server costs by eliminating over-provisioning.
It’s one of the biggest advantages in cloud application development services, especially when using auto-scaling features offered by cloud providers like AWS, Azure, or GCP.
2. High Fault Isolation
When one service crashes in a microservices setup, the rest of the system keeps running. This means your app stays available for users, even if part of it has issues. Fault isolation is essential in custom cloud application development, where uptime, fast recovery, and high availability are critical for smooth operations — just as in AI-driven wealth management software platforms that must provide real-time, uninterrupted portfolio tracking for users. It also simplifies incident management and improves reliability.
3. Faster Deployment and Updates
Each service in a microservices architecture can be built, tested, and deployed separately. This makes it easier to push updates or add features without touching the whole app. It fits well with DevOps, CI/CD pipelines, and agile development cycles, and supports the speed needed in cloud-native software delivery models.
4. Independent Teams and Flexible Tech Stac
Different teams can work on different services at the same time. They can even choose the programming languages, frameworks, or databases that suit their part best. This flexibility makes custom cloud application development more efficient and allows faster innovation across the entire app, especially in large, cross-functional development environments.
5. Smart Use of Resources
Microservices help reduce waste. You only use the exact amount of computing power needed for each service. This fine-grained resource allocation keeps your cloud bills lower and system performance smoother, especially under variable loads.
For anyone focusing on cloud application development, efficient resource use is a smart long-term strategy to control infrastructure costs and improve performance.
To sum up, microservices bring real value to cloud application development. They improve performance, resilience, and team productivity, helping businesses build stronger, more scalable, and adaptable cloud apps that support long-term growth.
You Might Also Like: Choosing Between Cloud-Native and Cloud-Based Applications
How Microservices Align with Cloud-Native Principles
Microservices connect naturally with cloud-native principles in cloud application development, helping businesses build scalable, agile, and resilient software architectures. This approach supports rapid delivery, fault isolation, and continuous improvement—key elements of successful digital transformation strategies.
The following points explain how microservices embody these principles:
1. Loosely Coupled Modular Services
Microservices split complex applications into small, independent units. Each service handles a specific business domain without shared databases or tight links. This aligns with cloud-native development ideals—such as modularity, autonomy, and loose coupling—by reducing interdependencies and simplifying updates, scaling, and maintenance. It enables domain-driven design (DDD), faster team velocity, and parallel development across services.
2. Containerization and Portability
Each microservice runs in its own container that bundles its code, configurations, libraries, and runtime dependencies. These containers operate seamlessly across development, staging, and production environments, and move effortlessly between public, private, multi-cloud, and hybrid cloud setups. This portability supports custom cloud application development, container orchestration, and consistent deployments using tools like Docker, Kubernetes, and OpenShift
3. Automated Orchestration and CI/CD
Microservices align perfectly with infrastructure automation, orchestration tools, and CI/CD deployment pipelines. Using orchestrators like Kubernetes, Helm, or Argo CD, containers can auto-scale, self-heal, and roll back if failures occur. Continuous integration and continuous delivery let teams deploy independently, reduce time-to-market, and push incremental improvements without disrupting the system. This automation underpins cloud-native software delivery models.
4. Resilient and Fault Tolerant Design
Microservices isolate failures within their own service boundaries. If one service fails, the rest of the application continues operating normally. Patterns like circuit breakers, bulkheads, retry logic, and service replication ensure the system is fault-tolerant and self-recovering. This architectural resilience is essential in cloud application development services, where 99.99% uptime, disaster recovery, and user experience continuity are top priorities.
5. Observability and Secure Inter‑Service Communication
A service mesh layer (like Istio or Linkerd) oversees secure, encrypted communication between microservices, providing TLS encryption, retries, rate limiting, and logging. Monitoring tools like Prometheus, Grafana, Jaeger, and OpenTelemetry offer detailed metrics, logs, and traces from every service. This observability gives teams deep visibility and helps manage complex distributed systems, which is essential for custom cloud application development at scale.
TenUp’s Take: To make the most of microservices in cloud application development, always start with a clear architecture plan. Break features into small, manageable services, and automate your CI/CD pipelines. This approach improves scalability, speeds up releases, and makes it easier to maintain complex systems as your product grows.
Challenges of Using Microservices in Cloud Application Development
Microservices support scalable cloud application development, but they come with technical challenges. Here are five common issues and practical ways to solve them without fluff or jargon.
1. Complex Service Management
In cloud application development, managing many small services becomes hard. Tasks like deployment, scaling, and routing grow complex and need automation for smooth performance across services—especially in cloud-native architectures.
How to Fix It: Use orchestration tools like Kubernetes for scaling and deployments. Add service meshes like Istio for traffic control and retries. Service discovery tools like Consul or Eureka help manage endpoints and reduce manual configurations for developers and ops teams. These are essential for delivering custom cloud application development services at scale.
2. Inter-Service Communication Issues
Microservices depend on APIs or events for communication. Network latency, request failures, and version mismatches can cause breakdowns that impact the overall stability of cloud-based applications.
How to Fix It: Use standardized protocols like REST or gRPC for clear interfaces. Add API gateways for routing, security, and rate limiting. Apply retry logic and circuit breakers with libraries like Hystrix. Messaging tools like Apache Kafka reduce direct dependencies and support asynchronous communication—key for robust cloud-native application development.
3. Data Consistency and Distributed Transactions
Each microservice often has its own database. This leads to challenges in maintaining data consistency across services, especially when a single business process involves multiple microservices in cloud application development.
How to Fix It: Apply the Saga pattern to manage workflows across services without distributed locks. Use event-driven architecture to update states asynchronously. Use idempotent operations and store event logs for traceability and recovery from partial failures or duplicates. These patterns are common in custom cloud-native applications.
4. Operational Complexity and Monitoring
With custom cloud application development, managing logs, metrics, and tracing across microservices is difficult. Without proper tooling, identifying the root cause of system issues becomes slow and complex, especially in distributed cloud environments.
How to Fix It: Centralize logs using ELK or EFK stacks. Collect metrics with Prometheus and visualize them in Grafana. Add distributed tracing tools like Jaeger or OpenTelemetry. Use health checks and alerts to track service status and performance in real time—these are critical for cloud-native observability.
5. Security in a Distributed System
More services mean more APIs and potential vulnerabilities. Ensuring proper encryption, authentication, and authorization across multiple internal and external endpoints is a major concern in microservices-based cloud application development.
How to Fix It: Secure each service with mutual TLS. Use OAuth2 and JWT for safe authentication. Deploy API gateways to control access and apply rate limits. Run regular audits, and enforce strict role-based access policies across all services and environments. These practices align with best-in-class cloud-native security standards.
Despite the hurdles, microservices can power efficient and resilient cloud application development. These challenges are solvable with smart tools, cloud-native design patterns, and planning built into the architecture.
Check out how TenUp used microservices architecture to future-proof an ERP in the Marine industry.
Best Practices for Implementing Microservices in Cloud Application Development
Effective microservices design is key to successful cloud application development. Below are 7 practical best practices to help teams build scalable and maintainable cloud-based solutions.
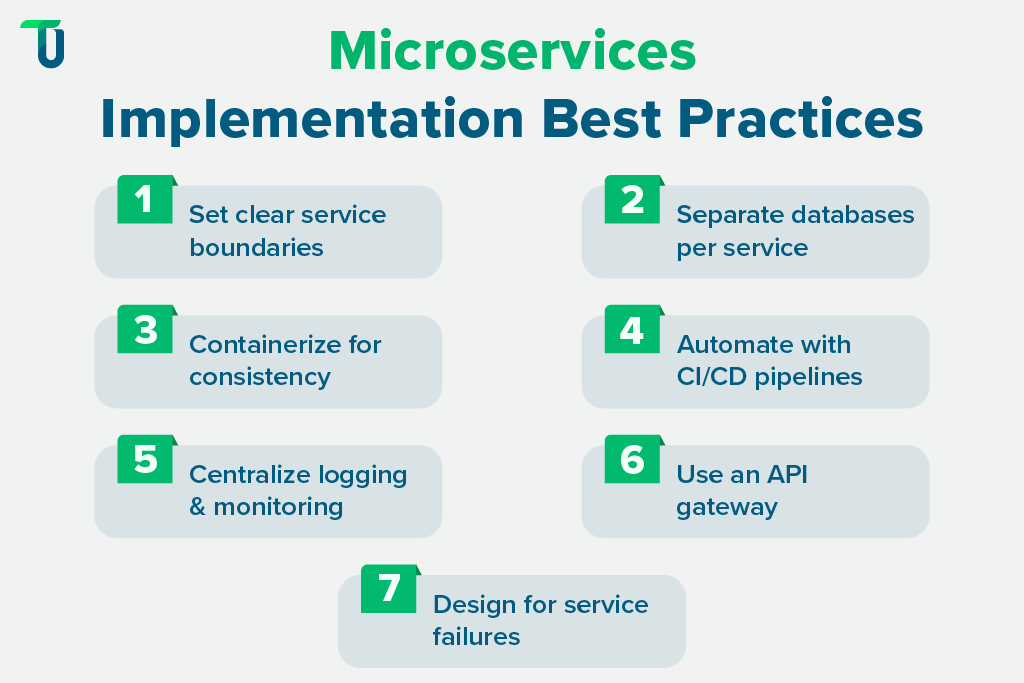
1. Define Clear Service Boundaries
Group features into services that reflect real business functions. This avoids tight coupling, improves code ownership, and simplifies scaling in cloud application development. It also supports faster updates and easier testing. This clarity is essential in cloud-native application architectures that demand autonomy and agility.
2. Use Separate Databases for Each Service
Assign each microservice its own data store to maintain loose coupling and reduce cross-service dependencies. This approach supports better data control in custom cloud application development and helps prevent system-wide failures. It’s also aligned with distributed system principles where service independence is key.
3. Containerize Microservices
Deploy microservices using containers to ensure consistency across development, testing, and production environments. Containerization improves portability and enables scalable cloud application development services using orchestration tools like Kubernetes. For cloud-native development, this ensures services can run reliably in any cloud or hybrid infrastructure.
4. Automate with CI/CD Pipelines
Set up CI/CD pipelines for each service to automate build, test, and deployment processes. This reduces manual errors, speeds up releases, and increases efficiency in cloud application development, especially for large, distributed teams. It also supports DevOps practices critical for continuous innovation in custom cloud software development.
5. Apply Centralized Logging and Monitoring
Use centralized tools for logs and metrics across all services. This improves visibility into system behavior, helps detect performance bottlenecks early, and is essential for managing modern cloud application development environments. Tools like Prometheus, Grafana, and OpenTelemetry can provide deep observability into microservices-based systems.
6. Use an API Gateway
Implement an API gateway to handle routing, authentication, rate limiting, and protocol translation. This simplifies communication across services and enhances security in cloud application development services with minimal overhead. API gateways are foundational for managing external and internal traffic in microservices architecture.
7. Plan for Service Failures
Design services to handle partial failures using patterns like retries, timeouts, and circuit breakers. This ensures your custom cloud application development remains stable and resilient even when individual components fail. Resilient design is key to meeting uptime and performance expectations in any scalable, cloud-native system.
Applying these best practices builds a strong foundation for cloud application development. They help teams deliver flexible, fault-tolerant, and maintainable microservices-based systems.
Also Read: Cloud Consulting Services to Accelerate DevOps & Software Delivery
Partner with TenUp for End-to-End Cloud Application Development
As we've discussed throughout this blog, the proper implementation of microservices is incredibly important for developing successful cloud applications. In addition to improved scalability and deployment speed, microservices also provide enhanced fault isolation, security, and overall system maintainability.
However, in order to fully realize these advantages, organizations will need the right technologies, processes, and skills to manage the complex, distributed systems required to support microservice architectures.
This is where TenUp comes into play. As an ISO 27001‑certified company and an AWS partner, we at TenUp Software Services provide end-to-end cloud application development solutions, from architecture planning and cloud migration to DevOps automation and serverless app development.
Partner with TenUp to Future-Proof Your Cloud Architecture
From design to deployment, we deliver end-to-end cloud solutions built for long-term performance and growth.
Frequently asked questions
What’s the difference between cloud application development and cloud migration?
Cloud application development builds new, cloud-native apps from the ground up using microservices, containers, and DevOps for high scalability, flexibility, and faster updates. Cloud migration moves existing apps to the cloud, often with minimal changes (lift-and-shift) or through refactoring to better use cloud features.
Can small teams use microservices in cloud apps successfully?
Yes. Small teams can thrive with microservices by using cloud-native tools like serverless, containers, and managed orchestration (e.g., Kubernetes). With clear API boundaries and modular design, they gain agility, faster deployment, and fault isolation without the overhead of monoliths. The key is to start small, automate early, and focus on domain-driven services.
When should teams choose monolith vs. microservices in cloud-native development?
Start with a monolith when building a simple app or MVP, because it’s faster to develop, deploy, and iterate. As the product grows in complexity or team size, microservices offer better scalability, fault isolation, and team autonomy. A modular monolith can help teams gradually evolve without the overhead of full microservices from day one.
How does multi-cloud or hybrid-cloud hosting impact microservices architecture?
Multi-cloud and hybrid-cloud enable better scalability, resilience, and vendor independence by distributing microservices across diverse environments. Using containers, CI/CD pipelines, and cloud-agnostic platforms like Kubernetes ensures portability, streamlines deployment, and avoids lock-in. However, this flexibility adds complexity in management, security, and API integration.
What role does API design play in cloud-based microservices?
API design ensures seamless communication between services using standards like REST or gRPC. Clear specs reduce versioning issues, while gateways add security, routing, and observability—critical for scaling resilient, cloud-native systems.
How can cloud application developers minimize vendor lock-in?
Developers can reduce vendor lock-in by using open standards like containers (OCI), Kubernetes, and infrastructure-as-code tools like Terraform. Avoid tightly coupled proprietary services, and design microservices with portable, cloud-agnostic interfaces for flexibility across providers.
What are the operational cost trade-offs of microservices in cloud apps?
While microservices enable precise scaling and resource control, they may raise costs due to overhead in orchestration, logging, monitoring, and data transactions. Teams should balance granularity against operational complexity.
Can low-code or no-code platforms support cloud-native microservices?
Yes. Modern low-code/no-code platforms can accelerate microservices prototyping, integration, and deployment through visual builders and API orchestration. They empower both developers and non-developers to create scalable cloud-native apps. However, for complex, deeply customized systems, traditional coding remains essential for full control and performance.

