What is Cloud Integration?
Cloud integration is the process of connecting cloud applications, platforms, and on-premise systems into one unified environment. iPaaS solutions such as MuleSoft, Dell Boomi, and Zapier provide API integration, supporting standards like REST, SOAP, and GraphQL. Using cloud integration tools and iPaaS platforms, it removes the need for manual tasks like exporting spreadsheets or copying files between applications by enabling enterprise cloud integration platforms that unify cloud and on-premise systems.
Additionally, with integration in place, data flows automatically between systems and stays accurate at all times. This helps teams access the same reliable information, save time, and avoid errors.
For modern business, it’s necessary because:
- Data stays synchronized across all applications, which ensures that decisions are based on real-time and correct information.
- Applications such as CRM, finance, and customer support platforms share records instantly, which speeds up workflows and reduces mistakes. This is one of the main benefits of cloud integration in business, improving collaboration and operational efficiency.
- Integration breaks down data silos and allows companies to scale easily, collaborate better, and serve customers faster, as a microservices architecture supports scalable cloud application development.
Cloud integration creates a connected business ecosystem. It enables agility, accuracy, and teamwork, which are vital for staying competitive in today’s digital environment. Learn how Supercloud architecture for unified cloud orchestration can enhance this connectivity across multiple cloud environments.
Key Components of Cloud Integration
Cloud integration services bring together multiple systems, data sources, and applications into one connected environment. Cloud integration tools and API integration solutions make this process seamless and reliable, as outlined below:
1. Applications and SaaS Platforms
Most businesses depend on SaaS tools such as Salesforce, HubSpot, Workday, or Microsoft 365. These applications manage vital business functions. However, they deliver maximum value only when connected to other platforms through cloud app integration with SaaS tools. Integration allows them to exchange data seamlessly and support end-to-end workflows.
2. Data and Databases
Data sits at the core of every business process. Cloud integration links structured data from databases and warehouses with unstructured data from sources such as emails, documents, or IoT devices. This unified access makes analytics more accurate and decision-making faster, while maintaining tenant data isolation for secure multi-tenant environments in SaaS applications.
3. APIs and Connectors
APIs function as digital bridges that let one system talk to another. REST, SOAP, or GraphQL APIs support different styles of communication. Pre-built connectors, available for popular apps, simplify the process by reducing development time and minimizing errors during integration.
4. Integration Platforms (iPaaS)
iPaaS provides a cloud-based environment designed to manage integrations at scale, offering enterprise-grade cloud governance and orchestration to simplify complex workflows such as data transformation and monitoring of integration flows. With iPaaS, businesses gain the flexibility to connect multiple applications and data sources.
Refine Operations and Data Flow with TenUp Cloud Services
Connect applications, access real-time data, and reduce manual work with our custom cloud integration solutions. Explore Our Services.
Types of Cloud Integration
Cloud integration can take different forms depending on how a business operates and what it needs to achieve. The four main types are described below.
A. Data Integration: Data integration combines information from various sources in a consistent view as well as helps keep accurate records between systems. For example, customer details from an e -commerce site flow to the analysis tools.
B. Application Integration: Integration of applications connects different software so that they work together in real time. A lead created in a CRM appears instantly on a marketing tool that reduces manual work and keeps workflows quickly and accurately.
C. Hybrid Integration: Hybrid integration binds cloud platforms with local systems. It allows inherited software to connect with cloud services and highlights the differences between multi-cloud and hybrid cloud. This protects past investments and supports smoother movement towards modern platforms.
D. Process Integration: Process integration aligns workflows into systems. In supply chains, ordering, inventory, collection, and shipping steps remain connected, which reduces delays and maintains efficient operations.
| Type | Focus | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Data Integration | Unifying data from multiple sources | Customer purchase data from an e-commerce site feeds into an analytics tool |
| Application Integration | Connecting software tools for real-time workflows | A lead created in CRM automatically appears in a marketing platform |
| Hybrid Integration | Linking cloud platforms with on-premise systems | Legacy ERP system connects with cloud-based finance software |
| Process Integration | Coordinating end-to-end business processes | Order entry triggers inventory update, billing, and shipping notifications |
Key Technologies and Protocols in Cloud Integration
Cloud integration depends on a set of main technologies that allow systems to talk, share, and protect data. These patterns guide how applications connect and how information flows safely. Here are some notable ones:
A. APIs (REST, SOAP, GraphQL)
APIs let applications software exchange data. REST is light and widely used in cloud services. SOAP remains important for rigid business needs. GraphQL allows flexible data requests, making it easier to obtain exactly what is needed from connected systems.
B. Messaging Protocols (MQTT, AMQP, JMS, Kafka)
Message protocols support communication between real-time applications. MQTT is ideal for IoT devices. AMQP provides reliable delivery. JMS standardizes Java messages. Kafka manages huge data flows and can power architectures oriented to events in modern environments, and tools like workflow automation with Apache Airflow help orchestrate these data pipelines efficiently.
C. Data Formats (JSON, XML, Avro, Parquet)
Data formats shape how information is stored and shared. JSON is light and used on most web tools and furniture. The XML supports many inherited platforms. Avro and Parquet are built for Big Data analysis and use– providing efficient storage and quick queries.
D. Security Protocols (OAuth 2.0, SAML, TLS/SSL)
Security protocols protect confidential information during integration. OAuth 2.0 protects API authorization, SAML allows a single sign-in between the systems, and TLS and SSL encrypt traffic in transit. This helps companies protect data and meet compliance needs.
These technologies form the basis of cloud integration. Together they ensure that applications remain connected, data remain consistent, and information flows safely.
Benefits of Cloud Integration
Benefits of cloud integration include faster access to real-time data, cost savings, stronger decision-making, and overall improved business efficiency. Businesses using cloud integration solutions for enterprises can scale operations smoothly. Organizations using CRM platforms like Salesforce or HubSpot see improved real-time data access, business agility, and collaboration across teams, while adhering to standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001 for data security. Here are the 6 key benefits of cloud integration.
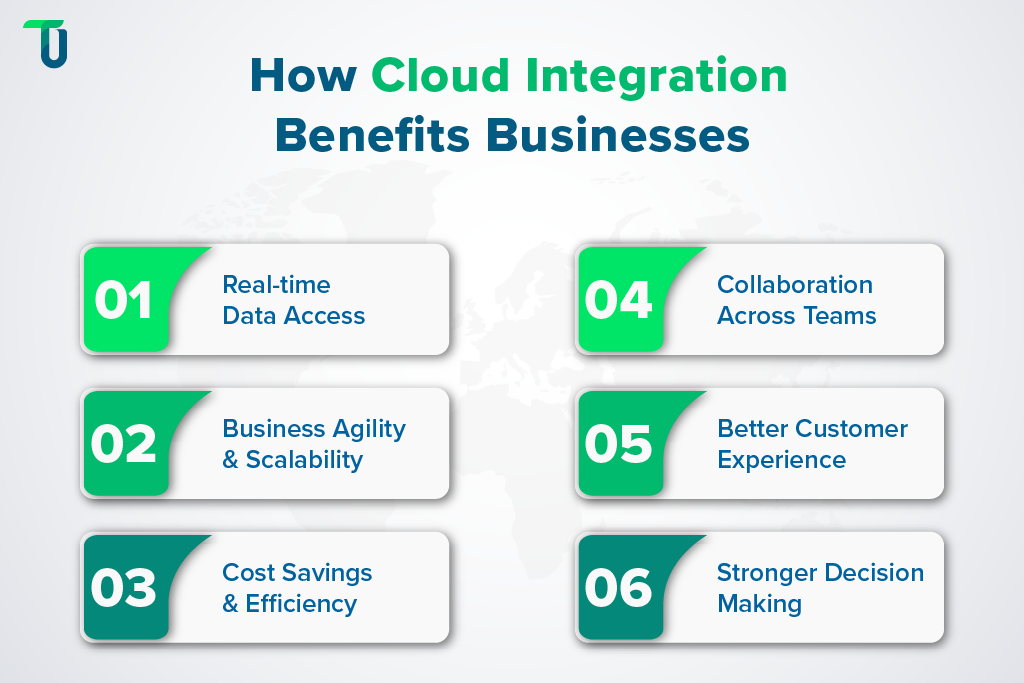
1. Real-Time Data Access
According to Integrate.io, companies adopting cloud data pipelines reduce time to insight by up to 60%. With cloud integration, records update instantly across all systems. When a CRM entry appears in dashboards and analytics, teams work from the same data and make faster decisions without waiting on reports.
2. Business Agility and Scalability
McKinsey reports firms can boost operational efficiency by 20‑25% through cloud adoption and integration. Cloud integration allows businesses to add or replace applications without disruption, and platforms adjust automatically to handle larger workloads and more complex data, which supports smooth growth.
3. Cost Savings and Efficiency
Organizations moving to the cloud and integrating systems reduce infrastructure and operational costs significantly. Cloud integration eliminates redundant tasks and errors by automating data flow, and employees can focus on higher-value work, while operations stay lean and processes run smoothly.
4. Collaboration Across Teams
Surveys show over 72% of companies say cloud solutions enhance collaboration. Cloud integration connects sales, finance, support, and marketing teams with shared data. As a result, teams communicate effectively, reduce delays, and execute projects faster, all while relying on accurate, real-time information.
5. Better Customer Experience
Research shows 68% of companies report better customer satisfaction with cloud systems. Cloud integration links CRM, support, and marketing platforms, so service agents access full customer history and sales teams have context. This connection delivers faster service and smoother experiences for customers.
6. Stronger Decision Making
Companies moving workloads to the cloud gain a clearer view of live data. Cloud integration ensures executives and managers receive up-to-date reports, budgets, and forecasts, allowing them to make decisions based on current information, reduce risks, and plan strategies with confidence.
All these benefits combined make cloud integration a powerful and must-have technology for modern businesses.
Related Read:
Why Cloud Migration Services Are Key for Agile, Secure Growth
Common Cloud Integration Challenges and How to Solve Them
As learned above, cloud integration offers a range of benefits. Despite its advantages, cloud integration challenges and solutions such as security, legacy system compatibility, and multi-cloud management can affect workflows. For example, integrating legacy ERP systems like SAP with modern cloud platforms can require middleware solutions, while managing multiple providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud introduces vendor dependency and compatibility issues. Understanding these challenges helps companies implement cloud integration services effectively.
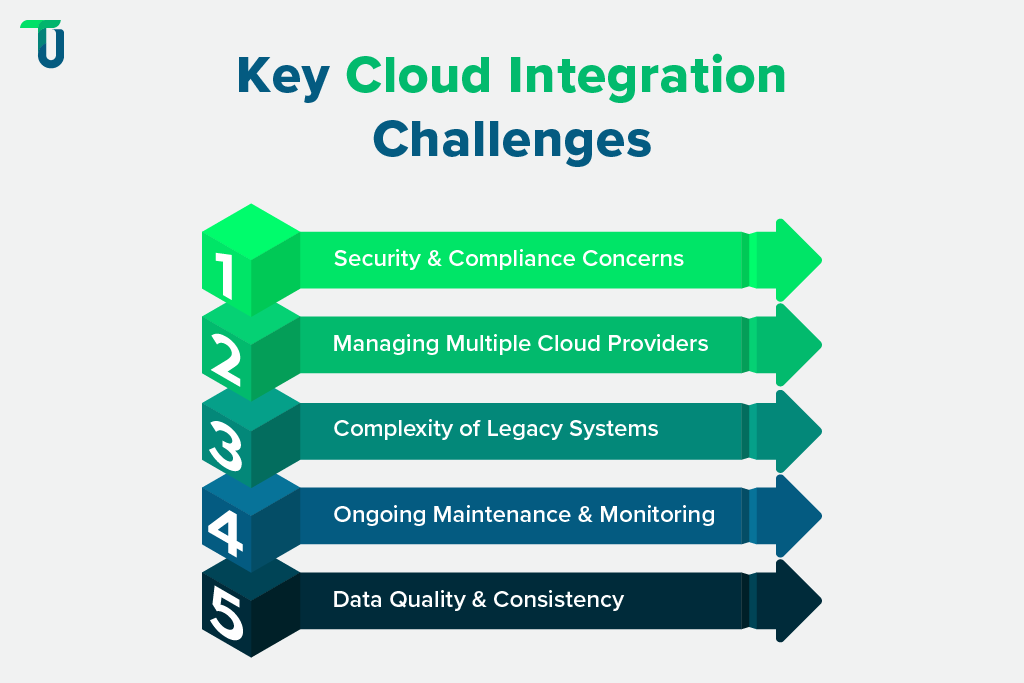
1. Security and Compliance Concerns
Transferring sensitive data across multiple cloud applications increases the risk of data breaches, unauthorized access, and regulatory violations. Companies must handle personal, financial, or health-related data carefully, ensuring secure data exchange during cloud migration and compliance with regulations like GDPR or HIPAA.
How to Address It:
- Encrypt data during transfer and storage to prevent unauthorized access.
- Apply strict user access controls and authentication policies.
- Conduct regular audits and compliance checks to identify gaps and fix them.
To encapsulate, addressing security and compliance challenges protects sensitive information and helps businesses operate safely and lawfully.
2. Managing Multiple Cloud Providers
Organizations often use several cloud providers for different applications. Coordinating integrations across these providers is complex, requires technical knowledge, and can create compatibility issues if platforms use different protocols or APIs.
How to Address It:
- Standardize integration protocols and use APIs compatible across platforms.
- Use centralized integration platforms or iPaaS to manage multiple connections.
- Monitor vendor performance, dependencies, and updates regularly.
As we can see, proper management of multiple cloud providers keeps integrations smooth and prevents errors or disruptions in workflows.
3. Complexity of Legacy Systems
Older on-premise systems may lack modern APIs or support contemporary data formats, making it difficult to integrate with cloud applications. Custom adapters or middleware may be needed, which adds time and cost to the process.
How to Address It:
- Implement middleware or adapters to bridge legacy systems with cloud applications.
- Plan a gradual migration of critical workloads to cloud platforms.
- Maintain clear documentation for data flows and system interactions.
Addressing legacy system complexity allows businesses to maintain continuity while modernizing without disrupting operations.
4. Ongoing Maintenance and Monitoring
Cloud integration is not a one-time effort, and systems need continuous monitoring to prevent failures, detect bottlenecks, and maintain performance—making cloud storage speed and reliability critical for long-term operational stability. Without oversight, integrations can break silently, causing data errors and operational issues.
How to Address It:
- Set up automated alerts for errors, failures, or performance issues.
- Conduct scheduled checks of system health, data flow, and connectivity.
- Maintain detailed logs and dashboards to track integration activity.
All in all, regular maintenance and monitoring ensure reliability, reduce risks, and keep systems functioning effectively over time.
5. Data Quality and Consistency
When systems store data in different formats or standards, inconsistencies occur, making managing data ingestion challenges in cloud integration an essential part of maintaining accurate and reliable workflows. Poor data quality affects reports, analytics, and decisions, which can mislead teams and cause operational problems.
How to Address It:
- Standardize data formats and structures across all applications.
- Apply validation, cleansing, and reconciliation procedures to correct errors.
- Implement master data management to maintain accuracy and consistency.
To put it together, like any other business process, cloud integration also comes with its own set of challenges and complexities. However, with careful planning, proper tools, and continuous monitoring, organizations can overcome these issues and reap the full benefits of cloud integration services.
Best Practices for Successful Cloud Integration
To reap the maximum benefits from cloud integration, businesses should follow proven strategies such as selecting the right iPaaS platforms, standardizing JSON or XML data formats, monitoring Kafka or MQTT messaging protocols, and designing integration-ready cloud architecture to handle growth effectively. Adopting these practices ensures compliance with ISO 27001 and SOC 2 security standards.
Here are 8 best practices to guide successful implementation.
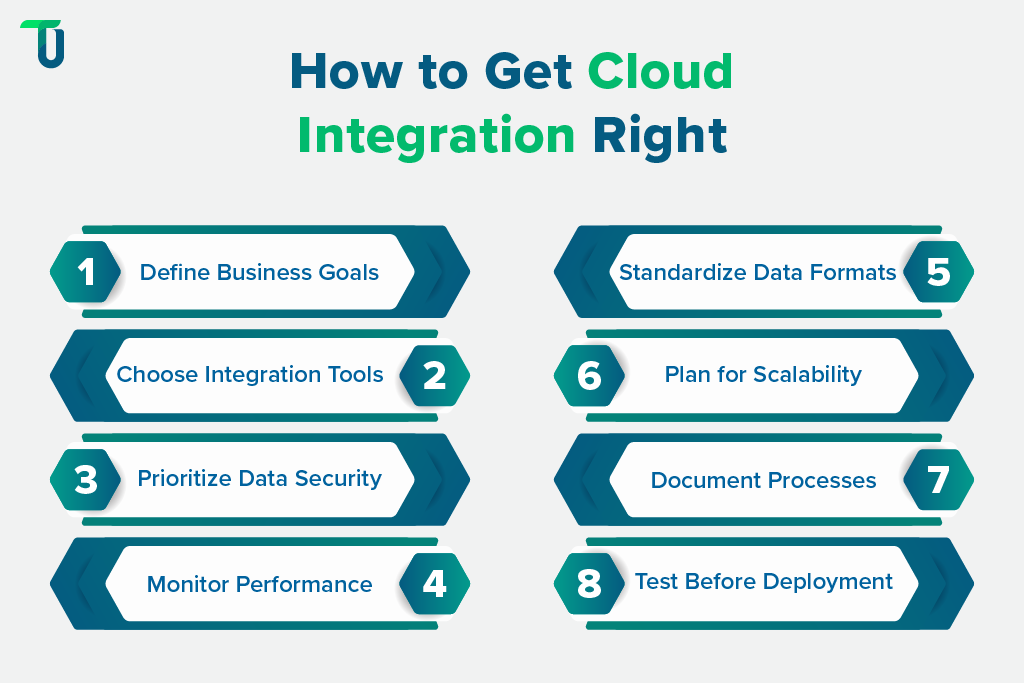
Tip #1: Define Clear Business Objectives
Start with a clear idea of what integration should achieve. Focus on outcomes like reducing manual data entry, enabling real-time reporting, and supporting better decision-making. Clear goals guide tool selection and project scope.
Tip #2: Choose the Right Integration Tools
Pick tools that fit your technical environment and scale. iPaaS solutions handle most integrations, while custom-built solutions may suit unique or complex business needs for seamless system connectivity.
Tip #3: Prioritize Security and Data Governance
Protect data through encryption, access controls, and compliance audits. Set governance rules to define who can view, modify, or transfer data across systems to prevent breaches and misuse.
Tip #4: Monitor Performance Continuously
Track integration health, data flows, and error logs. Regular monitoring identifies potential issues early, reduces downtime, and keeps systems running reliably without waiting for failures to occur.
Tip #5: Standardize Data Formats
Use consistent data formats across applications. Standardization reduces errors, simplifies integration, and ensures that information moves accurately between systems without mismatches or conflicts.
Tip #6: Plan for Scalability
Design integrations to handle growth in users, data, and applications, while considering a multi-cloud integration architecture to future-proof your environment and reduce operational disruptions.
Tip #7: Document Integration Processes
Maintain detailed documentation of integration steps, data sources, and dependencies. Proper documentation helps teams troubleshoot, train staff, and maintain workflows even when personnel change.
Tip #8: Test Before Deployment
Run tests in controlled environments before full deployment. Testing validates data flow, system compatibility, and error handling, reducing risks and preventing disruptions once the integration goes live.
A Complete Guide to Cloud-Based App Development
Cloud-Native vs. Cloud-Based Applications
Cloud Deployment Models: Public, Private, Hybrid, Multi-cloud
Optimize Your Business with TenUp Cloud Services Solutions
Cloud integration is essential for modern businesses aiming to streamline operations, enhance collaboration, and make data-driven decisions. By connecting various applications and platforms, companies can ensure real-time data access, improved efficiency, and scalability. However, successful implementation requires careful planning, the right tools, and ongoing monitoring to address challenges such as security, system compatibility, and data consistency.
That’s where we at TenUp step in. As an ISO 27001-certified company and trusted AWS partner, we bring deep expertise and hands-on experience in cloud solutions. From cloud application development to migration and serverless architectures, we offer a complete spectrum of cloud integration services tailored to your business needs. Get in touch today!
Empower Your Team with Secure and Scalable Cloud Services
Let TenUp handle cloud integration, migrations, and serverless setups so your business can operate smarter and faster. Get Started Today!
Frequently asked questions
What is cloud integration, and why is it essential for modern businesses?
Cloud integration connects cloud and on-premise systems into a unified environment, enabling real-time data flow, automated workflows, and better collaboration. It boosts efficiency, reduces costs, and supports scalable business growth.
How do cloud integration services differ from traditional software integration?
Cloud integration automates workflows, synchronizes data in real time, and scales easily via APIs and iPaaS platforms, while traditional integration relies on manual setup, on-premises hardware, and slower, rigid processes.
Which industries benefit most from cloud-based integration?
Industries with complex workflows, like finance, healthcare, retail, manufacturing, and logistics, benefit from cloud integration by streamlining operations, improving data accuracy, and enabling real-time insights.
What challenges can businesses face during cloud application integration?
Businesses often face challenges with legacy system compatibility, multiple cloud providers, data quality, security, and ongoing performance monitoring. Cloud integration solutions use standardized APIs, automation, and validation to address these issues.
How does hybrid cloud integration work, and why is it important?
Hybrid cloud integration connects on-premises systems with private and public clouds, enabling secure data sharing, scalable workloads, cost optimization, regulatory compliance, and flexible, uninterrupted business operations.
How can cloud integration software improve collaboration across teams?
Cloud integration software centralizes data and tools, enabling real-time access, seamless communication, and coordinated workflows, so teams can collaborate efficiently, reduce errors, and make faster, informed decisions.
What best practices ensure successful cloud integration implementation?
Successful cloud integration requires clear business objectives, choosing the right integration tools, standardizing data formats, prioritizing security, continuous monitoring, scalability planning, and thorough documentation. Testing integrations before deployment ensures smooth workflows and reliable operations across cloud environments.

